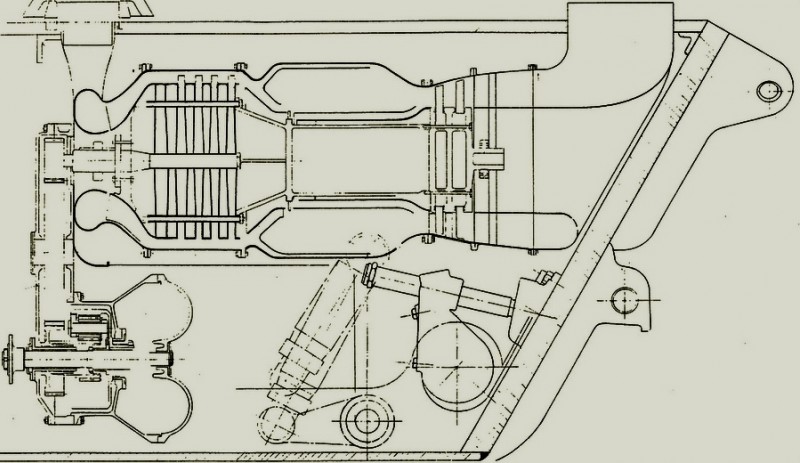
Pz.kpfw. 38h 735 (f)
Содержание:
Armaments
Main armament
Main article: KwK 38(t) (37 mm)
This vehicle has the same cannon as the Panzer 38(t) A. It is slightly better than the Pz.35(t)’s gun, but not by a significant amount, and therefore is used in exactly the same way. A 56 mm penetration APC-HE round, a 61 mm penetration APCBC-HE round, and a 93 mm penetration APCR round brings options for dealing with any type of ground target. The cannon easily dispatches most things it encounters, but may have trouble penetrating Valentines, the B1 bis and ter, Matildas, and Sherman 105s.
Machine guns
Main article: MG 37(t) (7.92 mm)
The tank has a coaxial 7.92 mm MG37(t) machine gun, which is useful for hosing down flak trucks, but not good for much else.
Историческая справка
-
Основная статья: История LT vz. 38
В конце 1937 года чехословацкая армия анонсировала конкурс на разработку лёгкого танка для замены LT vz.35. Фирма ČKD выставила на конкурс танк TNH-S, доработанный вариант экспортной боевой машины, созданной по иранскому заказу. В июле 1938 года, после испытаний и неоднократных переделок, машину приняли на вооружение под индексом LT vz.38 (лёгкий танк образца 1938 года). Танк срочно запустили в серийное производство, однако к моменту оккупации Чехословакии Германией успели построить всего около десятка.
LT vz.38 оказался лучшим чехословацким танком предвоенного периода. Кроме того, на начало войны это был лучший в мире лёгкий танк. Созданный под руководством инженера Алексея Сурина, он сочетал в себе хорошую манёвренность и мощное вооружение. Большой потенциал для модернизации позволил без ущерба для скорости нарастить толщину бронирования до 50 мм. Удачная конструкция LT vz.38 стала причиной того, что выпуск этого танка продолжился уже под немецким контролем. Всего было выпущено 1414 машин данного типа. Помимо немецкой армии, Pz.Kpfw. 38 (t) использовали венгры и румыны. Лицензию на производство LT vz.38 приобрели шведы, выпускавшие несколько изменённый танк под индексом Strv M/41.
В 1941 году LT vz.38, уже под немецким флагом и обозначением, пришлось встретиться с советскими Т-34 и КВ, в бою против которых у него было мало шансов. Справедливости ради, в это время по сравнению с советскими новыми танками устаревшими казались едва ли не все немецкие машины.
Operational history
In April 1940, the 342e CACC was sent to Norway after the German invasion of that country, having first been intended to form part of an expeditionary force to assist Finland in the Winter War. This autonomous company, equipped with fifteen «H 39″s, all with short guns, fought at Narvik, after having landed on 7 May. After the temporary liberation of that city, the twelve remaining vehicles were withdrawn to Britain on 8 June, where they joined the Free French, forming the 1e Compagnie de Chars de Combat de la France Libre. In 1940 and 1941, this 1e CCC fought against Vichy-troops in Gabon, and later in Syria.
Panzerkampfwagen 38H 735(f) used by the Germans in Yugoslavia in 1942
About 550 tanks were captured and used by the Germans as the Panzerkampfwagen 35H 734(f) or Panzerkampfwagen 38H 735(f). Most were used for occupation duty, but the independent 211e Panzerabteilung was deployed in Finland during Operation Barbarossa. Additional vehicles were sent to Finland as part of the independent Panzerkampfwagenzüge (tank platoons) 217, 218, and 219, which were attached to the 20th Mountain Army in February 1942. The platoons were the same as those of Panzerabteilung 211, consisting of one SOMUA S35 and four Hotchkiss tanks.
Like the French themselves, the Germans made no clear distinction between a «H 38» and a «H 39». The Germans fitted hatches to tanks equipped with a cupola. Some vehicles were modified to become munition carriers, artillery tractors (Artillerieschlepper 38H(f))s, or rocket-launchers (Panzerkampfwagen 35H(f) mit 28/32 cm Wurfrahmens). In 1942, 24 were converted into Marder I Panzerjägers or tank destroyers (using the 7.5 cm PaK40(Sf) auf Geschützwagen 39H(f)), and 48 into mechanised artillery, the 10.5 cm leFH18(Sf) auf Geschützwagen 39H(f). All were to be used by units in France. A special artillery observation vehicle was created, the Panzerbeobachtungswagen 38H (f). In June 1943, 361 Hotchkiss tanks were still listed in the German Army inventories as 37 mm gun tanks. This number had decreased to sixty in December 1944.
In 1943, the Germans, against objections, delivered nineteen «H 39″s to Bulgaria for training purposes when it proved to be impossible to find 25 unmodified Panzerkampfwagen Is, the type the Bulgarians really desired. After the war, these vehicles were used by police units. In 1944, the Germans delivered fifteen vehicles to Hungary and a small number to Croatia.
In North Africa, 27 vehicles (thirteen H 35s and fourteen «H 39″s) were officially serving in the 1e Régiment de Chasseurs d’Afrique and were allowed to remain there by the armistice conditions, and another five were hidden in Morocco. They fought the Allies during the opening stages of Operation Torch near Casablanca in November 1942, destroying four M3 Stuart light tanks. The regiment then joined the Allied cause and was re-equipped with M4 Shermans in the summer of 1943.
After the war, some Hotchkiss tanks were used by French security forces in the colonies and occupation forces in Germany. Ten «H 39s» were clandestinely sold to Israel and shipped from Marseilles to Haifa in 1948. At least one remained in service with the IDF until 1952.
История танка
Почему статья про Гочкисс H35 (фр. Hotchkiss H35)???
Ведь в немецком руководстве по опознанию иностранной военной техники «D50/12 Kennblaetter fremden Geraets Heft 12 Kraftfahrzeuge», датированном 21 марта 1941 г,танк получил обозначение в соответствии с заводской документацией фирмы Hotchkiss — «Panzerkampfwagen 38 H 735 (f) — frz. Hotchkiss 38»,так же был «Panzerkampfwagen 35 Н 734 (f) — frz. Hotchkiss 35». Но в отчетах и приказах использовалось краткое обозначение Pz.Kpfw.38 Н . Должна быть статья про лёгкий танк сопровождения R 35 (фр. Char léger d’accompagnement R35) — французский пехотный танк 1930-х годов.
Тут кое кто писал о историческом не соответствий,тоже неправильно…R 39 — вариант с новой длинноствольной пушкой SA38 которая появилась на танках поздних выпусков где SA 18 была заменена новой пушкой SA 38 того же калибра, но отличавшейся увеличенной длиной ствола и более мощными боеприпасами и, как следствие, возросшей до 701 м/с начальной скоростью снаряда и лучшей бронепробиваемостью, достигавшей 30 мм на дистанции в 1000 метров.со значительно лучшими противотанковыми качествами, выпущено 273 единиц…соответственно «трофейный» Гочкис имел такую пушку на вооружений.Достойный танк на своем уровне!
Operational history
In April 1940, the 342e CACC was sent to Norway after the German invasion of that country, having first been intended to form part of an expeditionary force to assist Finland in the Winter War. This autonomous company, equipped with fifteen «H 39″s, all with short guns, fought at Narvik, after having landed on 7 May. After the temporary liberation of that city, the twelve remaining vehicles were withdrawn to Britain on 8 June, where they joined the Free French, forming the 1e Compagnie de Chars de Combat de la France Libre. In 1940 and 1941, this 1e CCC fought against Vichy-troops in Gabon, and later in Syria.
Panzerkampfwagen 38H 735(f) used by the Germans in Yugoslavia in 1942
About 550 tanks were captured and used by the Germans as the Panzerkampfwagen 35H 734(f) or Panzerkampfwagen 38H 735(f). Most were used for occupation duty, but the independent 211e Panzerabteilung was deployed in Finland during Operation Barbarossa. Additional vehicles were sent to Finland as part of the independent Panzerkampfwagenzüge (tank platoons) 217, 218, and 219, which were attached to the 20th Mountain Army in February 1942. The platoons were the same as those of Panzerabteilung 211, consisting of one SOMUA S35 and four Hotchkiss tanks.
Like the French themselves, the Germans made no clear distinction between a «H 38» and a «H 39». The Germans fitted hatches to tanks equipped with a cupola. Some vehicles were modified to become munition carriers, artillery tractors (Artillerieschlepper 38H(f))s, or rocket-launchers (Panzerkampfwagen 35H(f) mit 28/32 cm Wurfrahmens). In 1942, 24 were converted into Marder I Panzerjägers or tank destroyers (using the 7.5 cm PaK40(Sf) auf Geschützwagen 39H(f)), and 48 into mechanised artillery, the 10.5 cm leFH18(Sf) auf Geschützwagen 39H(f). All were to be used by units in France. A special artillery observation vehicle was created, the Panzerbeobachtungswagen 38H (f). In June 1943, 361 Hotchkiss tanks were still listed in the German Army inventories as 37 mm gun tanks. This number had decreased to sixty in December 1944.
In 1943, the Germans, against objections, delivered nineteen «H 39″s to Bulgaria for training purposes when it proved to be impossible to find 25 unmodified Panzerkampfwagen Is, the type the Bulgarians really desired. After the war, these vehicles were used by police units. In 1944, the Germans delivered fifteen vehicles to Hungary and a small number to Croatia.
In North Africa, 27 vehicles (thirteen H 35s and fourteen «H 39″s) were officially serving in the 1e Régiment de Chasseurs d’Afrique and were allowed to remain there by the armistice conditions, and another five were hidden in Morocco. They fought the Allies during the opening stages of Operation Torch near Casablanca in November 1942, destroying four M3 Stuart light tanks. The regiment then joined the Allied cause and was re-equipped with M4 Shermans in the summer of 1943.
After the war, some Hotchkiss tanks were used by French security forces in the colonies and occupation forces in Germany. Ten «H 39s» were clandestinely sold to Israel and shipped from Marseilles to Haifa in 1948. At least one remained in service with the IDF until 1952.
Surviving vehicles
One Hotchkiss H35 and nine Hotchkiss H35s modifié 39 have survived until today. All of the modifié 39s were modified again by the Germans during WW2 . The sole surviving unmodified Hotchkiss H35 was discovered in December 2008, 200 meters off the coast, at Sainte-Cecile beach, Camiers, Pas-de-Calais, France. It is a turretless chassis, most probably a veteran of the Dunkerque gap fightings, which happened in May–June 1940. The tank was dredged in late 2008 thanks to the tide . The Musée des Blindés at Saumur plans to recover this tank in order to display it in the museum, but its recovery proves to be very difficult and costly.
Modules
Guns
| Gun | Penetration(mm) | Damage(HP) | Rate of fire(rounds/minute) | Dispersion(m/100m) | Aiming time(s) | Weight(kg) |
Price( ) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II | 3,7 cm Kw.K. 38 (t) L/47 | 42/74/18 | 40/40/45 | 26.09 | 0.41 | 1.7 | 100 | 2730 | |
| II | 2 cm Flak 38 | 39/51/18 | 11/11/45 | 130.43 | 0.45 | 1.4 | 110 | 3160 | |
| II | 4,7 cm Kw.K. (t) L/43 | 62/115/24 | 60/60/75 | 24 | 0.39 | 1.9 | 100 | 3460 |
Turrets
| Turret | Turret Armor (front/sides/rear)(mm) | Turret Traverse Speed(deg/s) | View Range(m) | Weight(kg) |
Price( ) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| III | Pz.Kpfw. 38 (t) Ausf. A | 25/15/15 | 32 | 310 | 1200 | 1620 | |
| IV | Pz.Kpfw. 38 (t) Ausf. E/F | 50/30/25 | 32 | 330 | 1800 | 4000 |
Engines
| Engine | Engine Power(hp) | Chance of Fire on Impact(%) | Weight(kg) |
Price( ) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II | Praga TNPS | 120 | 20 | 350 | 1150 | |
| IV | Praga EPA/3 | 200 | 20 | 470 | 10810 | |
| III | Praga EPA/2 | 140 | 20 | 470 | 4220 |
Suspensions
| Suspension | Load Limit(т) | Traverse Speed(gr/sec) | min | Weight(kg) |
Price( ) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II | Pz.Kpfw. 38 (t) Ausf. A | 9.9 | 32 | B/2 | 3200 | 620 | |
| III | Pz.Kpfw. 38 (t) Ausf. E | 12.3 | 35 | B/2 | 3200 | 1620 |
マップ
英語表記
英語表記ABBEYAIRFIELDBERLINCLIFFEL HALLUFEMPIRE’S BORDERENSKERLENBERGFISHERMAN’S BAYFJORDSGHOST TOWNGLACIERHIGHWAYHIMMELSDORFHINTERLANDKARELIAKHARKOVKLONDIKELAKEVILLELIVE OAKSMALINOVKAMANNERHEIM LINEMINESMINSKMOUNTAIN PASSMUROVANKANEBELBURGOVERLORDPARISPILSENPROKHOROVKAPROVINCEREDSHIRERUINBERGSAND RIVERSERENE COASTSIEGFRIED LINESTEPPESSTUDZIANKITUNDRAWESTFIELDWIDEPARK
削除されたマップDRAGON RIDGEHIDDEN VILLAGEICEBOUNDKOMARINMITTENGARDNORTH WESTPEARL RIVERSACRED VALLEYSEAPORTSEVEROGORSKSOUTH COASTSTALINGRADSWAMPWINDSTORM
日本語表記
日本語表記ウエストフィールドエーレンベルクエル・ハルフエンスクオーヴァーロード崖カレリアクロンダイクゴーストタウン鉱山高速道路後背地山岳路ジークフリート線修道院砂の川ステップストゥジャンキツンドラ帝国境界線ニーベルブルクのどかな海岸パリハリコフ飛行場ヒメルズドルフ氷河ピルゼンフィヨルドプロホロフカプロヴィンスベルリンマリノフカマンネルハイム線湖の村ミンスクムロヴァンカワイドパークライヴオーク漁師の港ルインベルクレッドシャイア
削除されたマップコマリンノースウェスト隠れ里南部海岸港竜の峠セヴェロゴルスク珠江湿地スターリングラード聖なる谷氷結暴風ミッテンガルド
Description
Hotchkiss H-39 light tank in Yad la-Shiryon Museum, Israel. 2005. The Char léger modèle 1935 H modifié 39; this vehicle has been modified by the Germans who fitted a cupola hatch.
As the Cavalry wanted an even better top speed, it was decided to bring to fruition experiments already conducted from October 1936 to install a stronger engine. A new prototype was made in 1937, with a 120 hp instead of a 78 hp engine. The hull was enlarged to accommodate it, and the track and the suspension elements were improved, raising the weight to 12.1 tons. This improved variant was faster, with a top speed of 36.5 km/h (22.6 mph), and much easier to drive. Therefore, it was first presented to the Commission d’Expérimentations de l’Infanterie on 31 January, 1939, to see whether the original negative decision could be changed. The commission indeed accepted the type, the Char léger modèle 1935 H modifié 39.
It was decided on 18 February to let it succeed the original version from the four hundred first vehicle onwards, which was just as well, as both in 1937 and 1938 an order had been made for 200 vehicles and production had already started. The total orders of the improved type was thereafter expanded to 900. The factory identifier, however, was the Char léger Hotchkiss modèle 38 série D, its predecessor having been the série B. The designation has caused much confusion; this was still officially the same tank as the «H 35», only in a later variant. However, even at the time, many began to refer to it as the 38 H or the 39 H.
The new subtype differed from the original one in having a raised and more angular engine deck (In later production, vehicles had crosswise instead of longitudinal ventilation slits on the right side.), road-range decreased to 120 km, closed idler wheels, tracks two centimetres wider at 27 cm, metal instead of rubber wheel treads, a silencer directed to the back, and larger, more reliable and effective ventilators.
Hotchkiss H39 on display at the Musée des Blindés in .
In early 1940, a modernisation program was initiated. Aside from the fitting of episcopes, tails, and some radio sets, this included the gradual introduction of a longer L/35 37 mm SA38 gun that had a much improved anti-tank capacity (30 mm penetration at 1000 m). About 350 vehicles were (re)built with the better gun, among them about fifty «H 35″s. The new gun became standard in the production lines in April. Before that change, the available new guns had, from January 1940, gradually been fitted to the tanks of platoon, company, and battalion commanders; about half of the commander vehicles in Hotchkiss units were so modified. It had been intended to fit the longer gun to all vehicles during the second half of 1940.
After the war, it was for a time erroneously assumed that «H 38» was the official name of the tank with the new engine, but without the new gun: «H 39» was the name of the type that had both major improvements. These mistakes are still common in many secondary literature. The «H 38» was, in fact, identical to the «H 39», and it is only correct to refer to the latter in an informal sense. Parallel to the development of an R 40, consideration was given, for a time, to the creation of an «H 40» by adopting the improved AMX suspension of the other vehicle. In the end, this option was rejected.
Operational history
In April 1940, the 342e CACC was sent to Norway after the German invasion of that country, having first been intended to form part of an expeditionary force to assist Finland in the Winter War. This autonomous company, equipped with fifteen «H 39″s, all with short guns, fought at Narvik, after having landed on 7 May. After the temporary liberation of that city, the twelve remaining vehicles were withdrawn to Britain on 8 June, where they joined the Free French, forming the 1e Compagnie de Chars de Combat de la France Libre. In 1940 and 1941, this 1e CCC fought against Vichy-troops in Gabon, and later in Syria.
Panzerkampfwagen 38H 735(f) used by the Germans in Yugoslavia in 1942
About 550 tanks were captured and used by the Germans as the Panzerkampfwagen 35H 734(f) or Panzerkampfwagen 38H 735(f). Most were used for occupation duty, but the independent 211e Panzerabteilung was deployed in Finland during Operation Barbarossa. Additional vehicles were sent to Finland as part of the independent Panzerkampfwagenzüge (tank platoons) 217, 218, and 219, which were attached to the 20th Mountain Army in February 1942. The platoons were the same as those of Panzerabteilung 211, consisting of one SOMUA S35 and four Hotchkiss tanks.
Like the French themselves, the Germans made no clear distinction between a «H 38» and a «H 39». The Germans fitted hatches to tanks equipped with a cupola. Some vehicles were modified to become munition carriers, artillery tractors (Artillerieschlepper 38H(f))s, or rocket-launchers (Panzerkampfwagen 35H(f) mit 28/32 cm Wurfrahmens). In 1942, 24 were converted into Marder I Panzerjägers or tank destroyers (using the 7.5 cm PaK40(Sf) auf Geschützwagen 39H(f)), and 48 into mechanised artillery, the 10.5 cm leFH18(Sf) auf Geschützwagen 39H(f). All were to be used by units in France. A special artillery observation vehicle was created, the Panzerbeobachtungswagen 38H (f). In June 1943, 361 Hotchkiss tanks were still listed in the German Army inventories as 37 mm gun tanks. This number had decreased to sixty in December 1944.
In 1943, the Germans, against objections, delivered nineteen «H 39″s to Bulgaria for training purposes when it proved to be impossible to find 25 unmodified Panzerkampfwagen Is, the type the Bulgarians really desired. After the war, these vehicles were used by police units. In 1944, the Germans delivered fifteen vehicles to Hungary and a small number to Croatia.
In North Africa, 27 vehicles (thirteen H 35s and fourteen «H 39″s) were officially serving in the 1e Régiment de Chasseurs d’Afrique and were allowed to remain there by the armistice conditions, and another five were hidden in Morocco. They fought the Allies during the opening stages of Operation Torch near Casablanca in November 1942, destroying four M3 Stuart light tanks. The regiment then joined the Allied cause and was re-equipped with M4 Shermans in the summer of 1943.
After the war, some Hotchkiss tanks were used by French security forces in the colonies and occupation forces in Germany. Ten «H 39s» were clandestinely sold to Israel and shipped from Marseilles to Haifa in 1948. At least one remained in service with the IDF until 1952.
Description
Hotchkiss H-39 light tank in Yad la-Shiryon Museum, Israel. 2005. The Char léger modèle 1935 H modifié 39; this vehicle has been modified by the Germans who fitted a cupola hatch.
As the Cavalry wanted an even better top speed, it was decided to bring to fruition experiments already conducted from October 1936 to install a stronger engine. A new prototype was made in 1937, with a 120 hp instead of a 78 hp engine. The hull was enlarged to accommodate it, and the track and the suspension elements were improved, raising the weight to 12.1 tons. This improved variant was faster, with a top speed of 36.5 km/h (22.6 mph), and much easier to drive. Therefore, it was first presented to the Commission d’Expérimentations de l’Infanterie on 31 January, 1939, to see whether the original negative decision could be changed. The commission indeed accepted the type, the Char léger modèle 1935 H modifié 39.
It was decided on 18 February to let it succeed the original version from the four hundred first vehicle onwards, which was just as well, as both in 1937 and 1938 an order had been made for 200 vehicles and production had already started. The total orders of the improved type was thereafter expanded to 900. The factory identifier, however, was the Char léger Hotchkiss modèle 38 série D, its predecessor having been the série B. The designation has caused much confusion; this was still officially the same tank as the «H 35», only in a later variant. However, even at the time, many began to refer to it as the 38 H or the 39 H.
The new subtype differed from the original one in having a raised and more angular engine deck (In later production, vehicles had crosswise instead of longitudinal ventilation slits on the right side.), road-range decreased to 120 km, closed idler wheels, tracks two centimetres wider at 27 cm, metal instead of rubber wheel treads, a silencer directed to the back, and larger, more reliable and effective ventilators.
Hotchkiss H39 on display at the Musée des Blindés in .
In early 1940, a modernisation program was initiated. Aside from the fitting of episcopes, tails, and some radio sets, this included the gradual introduction of a longer L/35 37 mm SA38 gun that had a much improved anti-tank capacity (30 mm penetration at 1000 m). About 350 vehicles were (re)built with the better gun, among them about fifty «H 35″s. The new gun became standard in the production lines in April. Before that change, the available new guns had, from January 1940, gradually been fitted to the tanks of platoon, company, and battalion commanders; about half of the commander vehicles in Hotchkiss units were so modified. It had been intended to fit the longer gun to all vehicles during the second half of 1940.
After the war, it was for a time erroneously assumed that «H 38» was the official name of the tank with the new engine, but without the new gun: «H 39» was the name of the type that had both major improvements. These mistakes are still common in many secondary literature. The «H 38» was, in fact, identical to the «H 39», and it is only correct to refer to the latter in an informal sense. Parallel to the development of an R 40, consideration was given, for a time, to the creation of an «H 40» by adopting the improved AMX suspension of the other vehicle. In the end, this option was rejected.
スペック(v1.9.0)
車体
| 耐久値 | 320 |
|---|---|
| 車体装甲厚(mm) | 40/40/40 |
| 最高速度(前/後)(km/h) | 37/16 |
| 初期重量(t) | 10.57 |
| 実用出力重量比(hp/t) | 7.1 |
| 本体価格 | 750G相当 |
| 修理費(Cr) | 約550 |
| 超信地旋回 | 不可 |
武装
| 名称 | 発射速度(rpm) | 弾種 | 平均貫通力(mm) | 平均攻撃力 | AP弾DPM | 精度(m) | 照準時間(s) | 総弾数 | 弾薬費(Cr) | 重量(kg) | 俯仰角 |
| 3,7 cm SA 38 L/34 | 26.25 | APAPCRHE | 416418 | 404045 | 1,050 | 0.4 | 1.71 | 200 | 148008 | 70 | -8°/+15° |
|---|
砲塔
| 名称 | 装甲厚(mm) | 旋回速度(°/s) | 視界範囲(m) | 重量(kg) |
| Pz.Kpfw. 38H 735 (f) | 40/40/40 | 47 | 330 | 1,000 |
|---|
エンジン
| 名称 | 馬力(hp) | 引火確率(%) | 重量(kg) |
| Hotchkiss | 75 | 20 | 200 |
|---|
履帯
| 名称 | 積載量(t) | 旋回速度(°/s) | 重量(kg) |
| Pz.Kpfw. 38H 735 (f) | 14.5 | 40 | 3,050 |
|---|
無線機
| 名称 | 通信範囲(m) | 重量(kg) |
| FuG 8 (f) | 525 | 50 |
|---|
乗員
| 1 | Commander(Gunner/Radio Operator/Loader) | 2 | Driver |
|---|
拡張パーツ
| × | Class1 | × | × | × | |||||
| Light | × | × | × |
隠蔽性
| 非発砲 | 発砲時 | |
|---|---|---|
| 静止時 | 14.25% | 4.13% |
| 移動時 | 10.72% | 3.11% |
車両に関する変更履歴
クリックで表示
| v0.9.20 | HDモデル化 |
| v1.9.0 | 総弾数を100発から200発に変更修理費用を50%ダウンHPを160から320に変更 |
General info
Survivability and armour
The Panzer 38(t) F has similarly bad survivability as the Pz.35(t) and Pz.38(t) A, but it boasts double the front hull and turret front armour. This makes it frontally immune to many reserve-tier guns, particularly Japanese, French, and Italian ones. But while it is harder to initially penetrate, its internal components are still weak. Angling your hull will increase your chances of surviving a hit.
Mobility
| Game Mode | Max Speed (km/h) | Weight (tons) | Engine power (horsepower) | Power-to-weight ratio (hp/ton) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | Stock | Upgraded | Stock | Upgraded | ||
| Arcade | 46 | 6 | 10.1 | 194 | 238 | 19.21 | 23.56 |
| Realistic | 42 | 6 | 111 | 125 | 10.99 | 12.38 |
The Pz.38(t) F has nearly identical mobility to the Pz.38(t) A, aside being slightly more sluggish. It is often wise to use this mobility to locate and acquire ambushing positions against the enemy.
Compatible Consumables
Pros and Cons
Cons:
- General low damage-tolerance requires teamwork and backup
- Weak armor
- Low Hit-Points
- Stock gun is weak, making it somewhat difficult to research better guns
- It cannot shoot through many tank’s fronts, it has to flank them
Performance
The Pz. 38 nA is a generally good all-round tank. Its weak armor and low hit-points limit the amount of damage it can take, but it is generally good at rushing a capture circle, spotting, or, with the L/60 gun (because it can penetrate a lot of tanks), reseting a capture. The tank’s different guns offer themselves to different strategies.
- The 2 cm Flak 38 machine gun is very effective at killing light tanks, because of its moderate reload and high capacity. It is limited with mediums and can almost never kill a heavy tank.
- The 4, 7 L/43 gun is a fast firing gun that does not give up as much penetration as the machine gun, making it more versatile than the Flak 38 or the L/60
- The 5 cm L/60 gun is a moderately fast gun that deals moderate damage (relative to the total single-shot damage capacity of each gun), but really excels in penetrating heavies and annoying them.
While the speed of this tank, especially with the engine upgrade, is very high, players should note where other supporting friendlies are, and avoid engagements without backup. Be careful driving quickly on low health, as this tank can actually «hop» over hills. Also, make sure to protect your tracks while engaging, as darting in and out of cover may be necessary.
History for this tank not found
Germany
| Light Tanks | ILeichttraktor • IIPz.Kpfw. 38H 735 (f) • IIPz.Kpfw. 35 (t) • IIPz.Kpfw. II • IIIPz.Kpfw. 38 (t) • IIIPz.Kpfw. III Ausf. A • IIIPz.Kpfw. II Ausf. J • IIIPz.Kpfw. II Ausf. G • IIIT-15 • IVPz.Kpfw. 38 (t) n.A. • IVPz.Kpfw. II Luchs • VVK 16.02 Leopard • VIVK 28.01 • VIISpähpanzer SP I C • VIIISpähpanzer Ru 251 |
| Medium Tanks | IIIPz.Kpfw. IV Ausf. A • IIIPz.Kpfw. S35 739 (f) • IVPz.Kpfw. III • IVPz.Kpfw. IV Ausf. D • VPz.Kpfw. III/IV • VPz.Kpfw. IV • VPz.Kpfw. IV hydrostat. • VPz.Kpfw. V/IV • VT-25 • VIPz.Kpfw. IV Schmalturm • VIVK 30.01 (P) • VIVK 30.01 (D) • VIVK 30.02 (M) • VIIPanther/M10 • VIIPanther I • VIIVK 30.02 (D) • VIIIIndien-Panzer • VIIIPanther II • IXE 50 • IXLeopard Prototyp A • XE 50 Ausf. M • XLeopard 1 |
| Heavy Tanks | IVPz.Kpfw. B2 740 (f) • IVDurchbruchswagen 2 • VVK 30.01 (H) • VIVK 36.01 (H) • VIITiger I • VIITiger (P) • VIITankenstein • VIIILöwe • VIIITiger II • VIIIVK 45.02 (P) Ausf. A • IXE 75 • IXVK 45.02 (P) Ausf. B • XE 100 • XMaus |
| Tank Destroyers | IIPanzerjäger I • IIIMarder II • IVHetzer • VStuG III Ausf. G • VIDicker Max • VIJagdpanzer IV • VIIE 25 • VIIE 25 «#1» • VIIJagdpanther • VIIIFerdinand • VIIIJagdpanther II • VIII8,8 cm Pak 43 Jagdtiger • VIIISnowstorm Jagdtiger 8.8 • IXJagdtiger • XJagdpanzer E 100 |
Light Tanks
| USA | IT1 Cunningham • IIT1E6 • IIT2 Light Tank • IIT7 Combat Car • IIIM22 Locust |
| UK | IICruiser Mk. III • IIICruiser Mk. IV • IVCovenanter • VCrusader |
| Germany | ILeichttraktor • IIPz.Kpfw. 38H 735 (f) • IIPz.Kpfw. 35 (t) • IIPz.Kpfw. II • IIIPz.Kpfw. 38 (t) • IIIPz.Kpfw. III Ausf. A • IIIPz.Kpfw. II Ausf. J • IIIPz.Kpfw. II Ausf. G • IIIT-15 • IVPz.Kpfw. 38 (t) n.A. • IVPz.Kpfw. II Luchs • VVK 16.02 Leopard • VIVK 28.01 • VIISpähpanzer SP I C • VIIISpähpanzer Ru 251 |
| USSR | IMS-1 • IIBT-2 • IIT-26 • IITetrarch • IIIBT-7 • IIIBT-SV • IIILTP • IIIM3 Light • IIIT-127 • IIIT-46 • IVA-20 • IVValentine II |
| France | |
| China | VIIType 62 • VIIType 62 Dragon |
| Japan | IRenault Otsu • IIType 95 Ha-Go • IIIType 98 Ke-Ni • IIIType 98 Ke-Ni Otsu • IVType 5 Ke-Ho |
| Czechoslovakia | |
| Sweden |
ja:Blitz:Pz38 NA
Operational history
In April 1940, the 342e CACC was sent to Norway after the German invasion of that country, having first been intended to form part of an expeditionary force to assist Finland in the Winter War. This autonomous company, equipped with fifteen «H 39″s, all with short guns, fought at Narvik, after having landed on 7 May. After the temporary liberation of that city, the twelve remaining vehicles were withdrawn to Britain on 8 June, where they joined the Free French, forming the 1e Compagnie de Chars de Combat de la France Libre. In 1940 and 1941, this 1e CCC fought against Vichy-troops in Gabon, and later in Syria.
Panzerkampfwagen 38H 735(f) used by the Germans in Yugoslavia in 1942
About 550 tanks were captured and used by the Germans as the Panzerkampfwagen 35H 734(f) or Panzerkampfwagen 38H 735(f). Most were used for occupation duty, but the independent 211e Panzerabteilung was deployed in Finland during Operation Barbarossa. Additional vehicles were sent to Finland as part of the independent Panzerkampfwagenzüge (tank platoons) 217, 218, and 219, which were attached to the 20th Mountain Army in February 1942. The platoons were the same as those of Panzerabteilung 211, consisting of one SOMUA S35 and four Hotchkiss tanks.
Like the French themselves, the Germans made no clear distinction between a «H 38» and a «H 39». The Germans fitted hatches to tanks equipped with a cupola. Some vehicles were modified to become munition carriers, artillery tractors (Artillerieschlepper 38H(f))s, or rocket-launchers (Panzerkampfwagen 35H(f) mit 28/32 cm Wurfrahmens). In 1942, 24 were converted into Marder I Panzerjägers or tank destroyers (using the 7.5 cm PaK40(Sf) auf Geschützwagen 39H(f)), and 48 into mechanised artillery, the 10.5 cm leFH18(Sf) auf Geschützwagen 39H(f). All were to be used by units in France. A special artillery observation vehicle was created, the Panzerbeobachtungswagen 38H (f). In June 1943, 361 Hotchkiss tanks were still listed in the German Army inventories as 37 mm gun tanks. This number had decreased to sixty in December 1944.
In 1943, the Germans, against objections, delivered nineteen «H 39″s to Bulgaria for training purposes when it proved to be impossible to find 25 unmodified Panzerkampfwagen Is, the type the Bulgarians really desired. After the war, these vehicles were used by police units. In 1944, the Germans delivered fifteen vehicles to Hungary and a small number to Croatia.
In North Africa, 27 vehicles (thirteen H 35s and fourteen «H 39″s) were officially serving in the 1e Régiment de Chasseurs d’Afrique and were allowed to remain there by the armistice conditions, and another five were hidden in Morocco. They fought the Allies during the opening stages of Operation Torch near Casablanca in November 1942, destroying four M3 Stuart light tanks. The regiment then joined the Allied cause and was re-equipped with M4 Shermans in the summer of 1943.
After the war, some Hotchkiss tanks were used by French security forces in the colonies and occupation forces in Germany. Ten «H 39s» were clandestinely sold to Israel and shipped from Marseilles to Haifa in 1948. At least one remained in service with the IDF until 1952.