Т-50
Содержание:
Ходовые характеристики
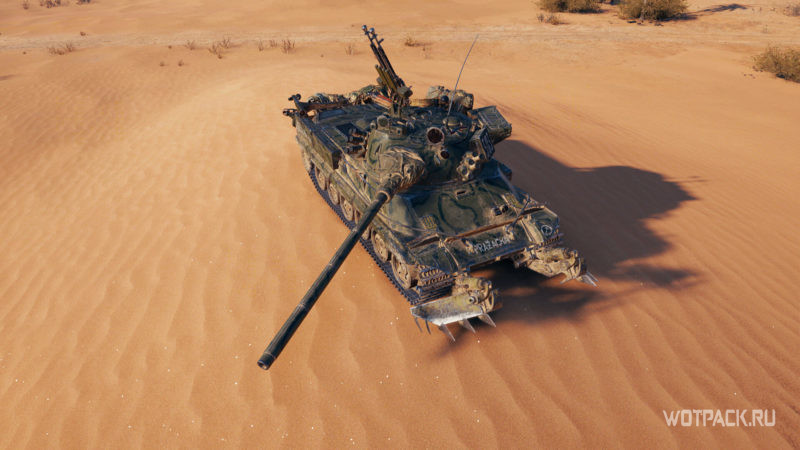
Здесь все просто замечательно — это САМЫЙ быстрый танк в игре. 72км/час обеспечат вам просто замечательную скорость. А если спускаться с горки, то и 85км/час легко можно выжать.
Радуют и динамические показатели машины — светлячок молниеносно разгоняется и огорчает противников своею маневренностью. Именно благодаря движку Т-50-2 является идеальным светом. Хотя, можно выразиться иначе — благодаря своему движку,Т-50-2 является идеальным БОЕВЫМ светом.

Этот танк может в схватке один на один разобрать практически любой танк в игре, конечно, при должном скилле командира. Основной критерий решения «могу ли я разобрать вон тот танк?» будет строится на том, насколько враг быстро может поворачивать башню. Впрочем, о тактике боя с высокоуровневыми противниками мы поговорим потом, сейчас же речь идет о ходовых характеристиках.
Благодаря своей подвижности, танкист может обеспечивать постоянный засвет требуемой точки. Но к скорости нужно относиться серьезно — так как с вводом физики разработчики перелопатили большинство карт, теперь можно отправиться в полет практически с каждой кочки. А 13 тонн, летящих по воздуху, это не очень мало:).
Срыв гусениц будет вашим постоянным противником. Дам маленький совет — если на вашем пути к цели множество крутых горок, не стоит сбрасывать скорость, лучше пересечь горку по диагонали. Тогда вы даже не подпрыгните и тем самым сбережете свои гусеницы.
Кроме снижения маневренности на 20%, физика преподнесла еще один сюрприз водителям Т-50-2 — те препятствия, которые преодолевались легко, теперь способны практически остановить танк. Бревна или тот же трактор нужно объезжать десятой дорогой:).
Историческая справка
-
Основная статья: История T20
T20 (англ. Medium Tank T20) — серия опытных средних танков, созданных в США в период Второй мировой войны. Программа по созданию нового среднего танка, превосходящего германские аналоги, предназначенного для замены M4, была начата в 1942 году. В мае—июне 1943 года были последовательно построены два прототипа танка T20 и два прототипа его усовершенствованного варианта, T22. Хотя испытания T20 и T22 продолжались вплоть до 1944 года, танки были сочтены не соответствующими требованиям армии. Кроме этого в 1943 году были разработан танк T23, оснащённый электромеханической трансмиссией. После успешных испытаний, было принято решение о серийном производстве T23, но после дальнейших испытаний танк был отвергнут армией и его производство ограничилось опытной партией из 10 серийных машин.
На танках серии T20 был испытан ряд технических новшеств, некоторые из которых в дальнейшем были внедрены в серийных танках; в частности, T22E1 стал первым в мире танком, оснащённым автоматом заряжания. Дальнейшее развитие серии T20 в 1943—1944 годах, в виде танков T25 и T26, привело к созданию танка M26, запущенного в серийное производство в ноябре 1944 года и в ограниченных масштабах использовавшегося в боях в Западной Европе весной 1945 года.
Suggested Equipment
Vents, Binocular Telescope, Coated Optics, Camouflage Net, Rammer
Historical Info
After the Spanish civil war, Red army leadership found T-26 tanks obsolete and ineffective, mostly due to their weak armor, therefore a development of a new tank was ordered. Two factories joined the competition, the OKMO design bureau in the Factory No. 185 (S.M. Kirov) and Kirov Factory No. 100, both located in Leningrad (the factories are often mistaken for each other because of very similar names).
The project of OKMO in the Factory No. 185 was known as Object 126 or T-126 SP, which later evolved into T-127, and eventually led to the T-50.
The competing Factory No. 100 came up with project known as Object 211, some sources name it «T-50-2». It was made in 1941 under the leadership of A. S. Yermolayev. Object 211 was slightly similar to the T-126 SP, it had 2×6 small wheels springed by torsions bars, but in comparison with the T-126 SP, the wheels were differently-made, distance between two whells was different etc. Object 211 also had a differently shaped and angled front armor, longer hull, and differently designed turret with much lower commander’s cupola. The armament and engine unit remained the same.
Unfortunately Object 211 did not win the competition because it did not bring any expressive advantages in comparison with the T-126 SP, it was only a little lighter.
The only prototype was deployed in the defense of Leningrad where it was probably destroyed.
Sources and External Links
https://www.panzernet.net/tankist/stranky/tanky/t50.php (CZ)
https://3v-soft.clan.su/news/ljogkij_tank_t_50/2010-09-08-150 (RU)
- Topic on official forum (RU)
- WOT Replays with Т-50-2
- // Wikipedia (RU)
Specifications
The original proposed weight of 35 tons was later increased to 40 tons. Upgunning was also needed and the caliber picked for the final version of the official demand was 100mm (the shell velocity was specified at 845 m/s, the vehicle was to carry 60 to 70 rounds). Further demands included sufficient protection while keeping excellent mobility on the battlefield, air-cooled diesel engine capable of operating under all climatic conditions. Maximum dimensions were set to 6,5m length, 3,2m width and 2,8m height, while clearance was to be 500mm. Armor thickness was set to 65mm frontal, 40mm sides and rear and everything else 20 to 30mm. The hull was to be welded.
Secondary armament was set to a 12,7mm AA machinegun (apparently Soviet DshkM) with 1000 rounds, a hull-mounted 7,62mm machinegun and a coaxial 7,62mm machinegun (both were supposed to be newly designed Czechoslovak machineguns with 3600 rounds for both).
Т-45 в игре
Исследование и прокачка
Эта машина является премиум техникой и не требует прокачки дополнительных модулей, она имеет «Элитный» статус, приносит больше кредитов и опыта за каждый бой, а также обладает рядом других преимуществ.
Боевая эффективность
- Достоинства:
- лучшая скорость поворота среди одноклассников;
- высокий показатель разового урона;
- неплохое бронепробитие;
- неплохая лобовая броня.
- Недостатки:
- посредственная динамика;
- посредственная точность;
- долгое сведение;
- малые УВН;
- перегруженность командира;
- частая критуемость двигателя.
Экипаж
- Боевое братство улучшит характеристики танка.
- Ремонт ускорит починку поврежденных модулей.
- Шестое чувство поможет определить, обнаружен ли танк или нет.
- Король бездорожья улучшит подвижность по слабым грунтам.
Оборудование, снаряжение и боекомплект
ББ40
БП26
ОФ
- Оборудование
- Просветленная оптика даст прибавку к обзору как стоя, так и в движении.
- Улучшенная вентиляция даст небольшой бонус к характеристикам танка.
- Усиленные приводы наводки ускорят сведение орудия.
- Снаряжение
Стандартный набор снаряжения: ремкомплект, аптечка и огнетушитель.
- Боекомплект
Основные снаряды — бронебойные. Подкалиберные стоит заряжать для встреч с бронированными противниками. Осколочно-фугасные снаряды такого калибра неэффективны.
История изменений
-
Основная статья: История изменений Т-45
История изменений
- Обновление 0.9.15
Добавлен для тестирования участникам Супертеста.
- Обновление 0.9.15.1
Танк введён в игру в качестве подарка на шестилетие World of Tanks.
- Обновление 1.9
- Боезапас изменён с 66 до 130 снарядов.
- Стоимость ремонта уменьшена на 50%.
- Прочность изменена с 140 до 280 единиц.
Production history
T-50 with Finnish markings at Parola tank museum
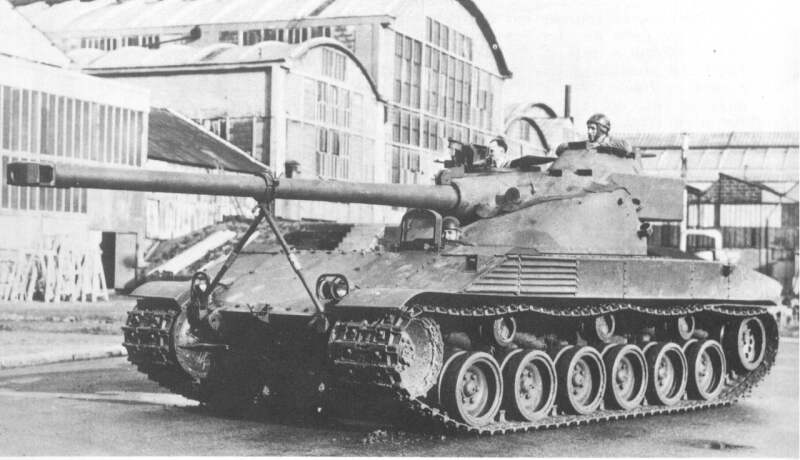
The T-50 was a light tank developed on the eve of World War II for the Red Army. The experience of the Spanish Civil War led to an effort to upgrade or replace the large Soviet tank fleet. Prior to 1939, most tanks in Red Army service were improved versions of foreign designs. For example, the most numerous tank, the T-26 light infantry tank, was a copy of the British Vickers 6-Ton tank with a Soviet-designed turret and 45 mm gun. However, just prior to and during the war, the USSR developed new light, medium and heavy tanks of wholly indigenous design. The T-50 light tank was intended to replace the T-26 infantry tank; in prewar planning, the T-50 was intended to become the most numerous Soviet tank, operating alongside the BT fast tank.
Development of the T-50 started as the SP project (Soprovzhdeniya Pekhoty, ‘Infantry Support’) in 1939 at the OKMO design bureau in the S.M. Kirov Factory Number 185 in Leningrad, under the direction of S. Ginzburg and L. Troyanov. Initial prototypes, called T-126 and T-127, were not much improved over the T-46-5 project which had been abandoned earlier that year, but the heavier T-126 was selected for further development. The design bureau was gutted during the Great Purge, and was unable to continue the project, so it was transferred to the K.E. Voroshilov Factory Number 174 in May 1940. Troyanov completed the T-50 design in January 1941 and production was authorized, but due to technical problems, it was unable to proceed. In the meantime, a replacement for the BT fast tanks was developed and built at the KhPZ factory in Ukraine, which exceeded its original programme. The result was the very capable and economical T-34 medium tank.
After the German invasion, Operation Barbarossa in June, tank factories were ordered to be transferred to the Urals. Part of OKMO was moved to Omsk after September, and production was finally begun. The T-50 was of an excellent design, but still suffered from technical problems, and at that time was found to be as expensive to produce as the more capable T-34. Much simpler T-60 light tanks were already being mass-produced. A total of 69 T-50 tanks were built (only 48 of them armed), before production ended in January 1942.Some further infantry tank design work on a prototype, called the T-45, continued at Factory Number 174 and the Kirovskiy Factory Number 100. But faced with the need to accelerate T-34 production, and due to a lack of interest from troops in the field, the Soviet infantry tank concept was abandoned.
Joint Cooperation
By the end of January, the shape of the hull was also discussed, including the number of roadwheels (ČKD had 5 pairs, Škoda had 6 pairs). Apparently, the 6-pair solution was adopted after some pressure from military liaison Maj.Hajšman. It was also decided that one entire prototype hull from armor steel would be produced by VŽKG (Vítkovice steelworks), while three more hulls from regular steel would be produced by Škoda. Škoda and ČKD would then cooperate on further development, while the turret would be developed exclusively by Škoda. Each company would then independently develop the engine, the transmission, drivetrain, steering mechanism, pedals, seats, fuel tanks and engine access ports. Engine air filters were to be developed by ČKD, while Škoda was to develop the suspension, ventilation and electric wiring. Furthermore, both companies were tasked with solving the implementation of the Soviet V-2 engine as a stopgap measure, because the high-power diesels still remained only on paper. What it meant in total was that Škoda would do most of the work, because ČKD was tasked also with the development of the universal LP chassis (light chassis for light tank/light tank destroyer/light SPG use).
On 15.2.1950, the number of planned prototypes was reduced to three (two from soft steel, one from armor steel). Furthermore, each company was to build two prototypes of their engines (Škoda – 16 cylinder AHK, ČKD – 16 cylinder AXK) with transmissions and ČKD was to solve the issue of implementing the Soviet V-2 engine. TVP transmission was actually built and tested in 1949 on a T-34/85 tank (as a part of the T-34/85 upgrade program) and the results were promising. The suspension was now planned to be a torsion bar one, but there were problems with their manufacture. Even though ČKD was developing their own engine air filters, Škoda came up with a plan to use captured Panther air filters. ČKD in turn came up with a proposal to use hydraulic gun elevation control and Ing.Surin came with a plan to introduce a mechanical automatic loader, but both plans were declined by the military representatives.
Ссылки
- Ресурсы World of Tanks
- Танковедение
- Тема на официальном форуме
- Записи боев на T69
- В сети Интернет
- T69 // Википедия
- Т69. Обзор танка от Slon Cruz // YouTube
Техника США
| Лёгкие танки | I T1 Cunningham • II M2 Light Tank • II T1E6 • II T2 Light Tank • II T7 Combat Car • III M22 Locust • III M3 Stuart • III MTLS-1G14 • IV M5 Stuart • V M24 Chaffee • V M7 • VI T21 • VI T37 • VII T71 CMCD • VII T71 DA • VIII T92 • VIII M41 Walker Bulldog • IX T49 • X XM551 Sheridan |
| Средние танки | II T2 Medium Tank • III M2 Medium Tank • IV T6 Medium • IV M3 Lee • V M4 Improved • V M4A2E4 Sherman • V M4A1 Sherman • V Ram II • VI M4A3E8 Fury • VI M4A3E8 Thunderbolt VII • VI M4A3E8 Sherman • VI M4A3E2 Sherman Jumbo • VII T26E3 Eagle 7 • VII T20 • VII T23E3 • VIII T25 Pilot Number 1 • VIII TL-1 LPC • VIII M46 Patton KR • VIII M26 Pershing • VIII T26E4 SuperPershing • VIII T26E4 SuperPershing FL • VIII T69 • VIII T95E2 • IX M46 Patton • X M48A5 Patton • X M60 • X T95E6 |
| Тяжёлые танки | V T14 • V T1 Heavy Tank • VI M6 • VII King Tiger (захваченный) • VII T29 • VIII Chrysler K • VIII Chrysler K GF • VIII T26E5 • VIII T26E5 Patriot • VIII M54 Renegade • VIII M6A2E1 • VIII T32 • VIII T34 • VIII T34 B • IX AE Phase I • IX M103 • IX T54E1 • X T110E5 • X T57 Heavy Tank |
| ПТ-САУ | II T3 HMC • III T56 GMC • IV M8A1 • IV T40 • V M10 Wolverine • V T67 • VI T78 • VI M18 Hellcat • VI M36 Jackson • VII M56 Scorpion • VII T28 Concept • VII Super Hellcat • VII T25/2 • VII T25 AT • VIII TS-5 • VIII T28 • VIII T28 Prototype • IX T30 • IX T95 • X T110E3 • X T110E4 |
| САУ | II T1 HMC • III T18 HMC • III M7 Priest • IV T82 HMC • IV M37 • V M41 HMC • VI M44 • VII M12 • VIII M40/M43 • IX M53/M55 • X T92 HMC |
Средние танки
| Техника СССР | III Т-29 • IV А-32 • IV Т-28Э с Ф-30 • IV Т-28 • V Матильда IV • V Т-34 экранированный • V Т-34 • VI А-43 • VI Т-34-85М • VI Т-34-85 Rudy • VI М4-А2 Шерман Лозы • VI Т-34-85 • VII А-44 • VII КВ-13 • VII Т-43 • VIII Объект 416 • VIII Т-54 первый образец • VIII Т-44-100 (Б) • VIII Т-44-100 (К) • VIII Т-44-100 (Р) • VIII Т-44-100 (У) • VIII СТГ • VIII СТГ Гвардеец • VIII Т-44 • IX Объект 430 Вариант II • IX Объект 430 • IX Т-54 • X Объект 140 • X Объект 907 • X Т-22 ср. • X К-91 • X Объект 430У • X Т-62А |
| Техника Германии | III Großtraktor — Krupp • III Pz.Kpfw. IV Ausf. A • III Pz.Kpfw. S35 739 (f) • IV Pz.Kpfw. III Ausf. J • IV Pz.Kpfw. IV Ausf. D • IV VK 20.01 (D) • V Pz.Kpfw. III Ausf. K • V Turán III prototípus • V Pz.Kpfw. III/IV • V Pz.Kpfw. IV hydrostat. • V Pz.Kpfw. V/IV • V Pz.Kpfw. V/IV Alpha • V Pz.Kpfw. IV Ausf. H • V Pz.Kpfw. T 25 • V VK 30.01 (H) • VI Pz.Kpfw. IV Schmalturm • VI VK 30.01 (D) • VI VK 30.02 (M) • VII Panther/M10 • VII Panther • VII VK 30.02 (D) • VIII Panther mit 8,8 cm L/71 • VIII Panzer 58 • VIII Schwarzpanzer 58 • VIII Panzer 58 Mutz • VIII M48A2 Räumpanzer • VIII Indien-Panzer • VIII Panther II • IX E 50 • IX T 55A • IX Kampfpanzer 50 t • IX Leopard Prototyp A • X E 50 Ausf. M • X Leopard 1 |
| Техника США | II T2 Medium Tank • III M2 Medium Tank • IV T6 Medium • IV M3 Lee • V M4 Improved • V M4A2E4 Sherman • V M4A1 Sherman • V Ram II • VI M4A3E8 Fury • VI M4A3E8 Thunderbolt VII • VI M4A3E8 Sherman • VI M4A3E2 Sherman Jumbo • VII T26E3 Eagle 7 • VII T20 • VII T23E3 • VIII T25 Pilot Number 1 • VIII TL-1 LPC • VIII M46 Patton KR • VIII M26 Pershing • VIII T26E4 SuperPershing • VIII T26E4 SuperPershing FL • VIII T69 • VIII T95E2 • IX M46 Patton • X M48A5 Patton • X M60 • X T95E6 |
| Техника Франции | III D2 • III Somua S35 • IV SARL 42 • V Renault G1 • VI Bretagne Panther • VIII Bat.-Châtillon Bourrasque • VIII Lorraine 40 t • VIII AMX Chasseur de chars • VIII M4A1 Revalorisé • IX AMX 30 1er prototype • IX Char Futur 4 • IX Bat.-Châtillon 25 t AP • X Bat.-Châtillon 25 t • X AMX 30 B |
| Техника Великобритании | I Vickers Medium Mk. I • II Vickers Medium Mk. II • III Vickers Medium Mk. III • IV Matilda • IV Grant • IV AC 1 Sentinel • V Cavalier • V Sherman III • V Matilda Black Prince • VI Sherman Firefly • VI Cromwell • VI AC 4 Experimental • VI Cromwell B • VI Sherman VC Firefly • VII Comet • VIII Centurion Mk. I • VIII FV4202 • VIII Chieftain/T95 • VIII Centurion Mk. 5/1 RAAC • VIII Chimera • IX Centurion Mk. 7/1 • X Centurion Action X |
| Техника Китая | V Type T-34 • VI Type 58 • VII T-34-1 • VIII Type 59 • VIII T-34-2 • VIII T-34-3 • VIII 59-Patton • VIII Type 59 G • IX WZ-120 • X • X 121B |
| Техника Японии | II Chi-Ni • II Type 89 I-Go/Chi-Ro • IV Type 1 Chi-He • V Type 3 Chi-Nu • V Type 3 Chi-Nu Kai • VI Type 4 Chi-To • VII Type 5 Chi-Ri • VIII STA-1 • VIII STA-2 • IX Type 61 • X STB-1 |
| Техника Чехословакии | IV ST vz. 39 • V Škoda T 24 • VI Škoda T 40 • VI Škoda T 25 • VII Konštrukta T-34/100 • VIII TVP VTU Koncept • VIII Škoda T 27 • IX Škoda T 50 • X TVP T 50/51 |
| Техника Швеции | IV Lago • V Strv m/42 • VI Strv m/42-57 Alt A.2 • VI Strv 74 • VII Leo • VIII Strv 81 • VIII Primo Victoria • VIII Lansen C • VIII UDES 14 Alt 5 • IX UDES 16 • X UDES 15/16 |
| Техника Польша | V 25TP KSUST II • VI Pudel • VI 40TP Habicha • VI T-34-85 Rudy |
| Техника Италии | II M14/41 • III M15/42 • IV P26/40 • V P.43 • VI P.43 bis • VII P.43 ter • VIII Progetto M35 mod. 46 • VIII P.44 Pantera • IX Prototipo Standard B • X Progetto M40 mod. 65 |
Modules
Guns
| Gun | Penetration(mm) | Damage(HP) | Rate of fire(rounds/minute) | Dispersion(m/100m) | Aiming time(s) | Weight(kg) |
Price( ) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IX | 100 mm A20 | 205/240/50 | 320/320/420 | 8 | 0.36 | 2.5 | 3000 | 205000 | |
| IX | 100 mm R11 | 230/269/50 | 320/320/420 | 7.5 | 0.36 | 2.3 | 3800 | 224000 | |
| X | 100 mm AK1 | 248/310/50 | 320/320/420 | 7.02 | 0.35 | 2.2 | 2600 | 275000 |
Turrets
| Turret | Turret Armor (front/sides/rear)(mm) | Turret Traverse Speed(deg/s) | View Range(m) | Weight(kg) |
Price( ) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIII | Škoda T 50 (1949) | 100/100/100 | 38 | 380 | 8600 | 32700 | |
| IX | Škoda T 50 (1950) | 120/80/60 | 42 | 400 | 9000 | 58000 |
Engines
| Engine | Engine Power(hp) | Chance of Fire on Impact(%) | Weight(kg) |
Price( ) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IX | Škoda 16 AH 145 | 750 | 12 | 1400 | 82000 | |
| X | Škoda AHK | 1000 | 10 | 1700 | 110000 |
Suspensions
| Suspension | Load Limit(т) | Traverse Speed(gr/sec) | min | Weight(kg) |
Price( ) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIII | Škoda T 50 (1949) | 38.5 | 38 | 12000 | 32000 | ||
| IX | Škoda T 50 (1950) | 43 | 42 | 12000 | 62700 |
Тактика игры
Первое, что нужно понять, купив Т-50-2 — МЫ МОЖЕМ РЕШИТЬ ИСХОД БОЯ, ЕСЛИ УЦЕЛЕЕМ. Выжить до начала завершающей стадии боя очень сложно, множество соблазнов, но если это сделать, мы можем решить исход сражения, вовремя уничтожив артиллерию или, например, можно отвлечь и уничтожить того тяжа, который заходит в спину оставшемуся среднему танку.
Но в погоне за сохранностью собственной жизни не следует стоять весь бой в кустах и смотреть, как враги уничтожают союзников одного за другим.
Первое, что нужно сделать в сражении — засветить вражеские танки, чтобы по ним отработала союзная артиллерия
Но светить нужно очень осторожно, не стоит ломиться на вражескую базу, там вы точно не выживете. Осторожно подсветили и уехали назад.
Переходим к противостоянию врагам
Как я уже говорил, множество игроков недооценивают вражеского советского светлячка. Внимательно следите за миникартой и общим ходом сражения — если вы где-то заметили одинокий вражеский танк, нужно сразу решить — насколько он подвижный? Если противник не может похвастаться чрезвычайно быстрой башней, смело едем к нему — это очередная жертва. Подъехав к врагу, просто начинаем обстреливать его из своего орудия. Во время обстрела нужно обязательно следить за тем, куда смотрит орудие супостата.
Как только противник ощутил страдания от неуклонно уменьшающихся ХП, он попытается вас уничтожить. Разрушить его планы можно простым шагом — просто крутимся вокруг врага, не давая ему в нас прицелиться. В рэндоме немногие игроки доворачивают корпус, поэтому крутить наивных танкистов до безобразия легко. Если все же вы видите, что орудие скоро будет наведено на вас, сделайте ход конем — резко сдайте назад. В 80% случаев враг просто не успеет среагировать и снаряд уйдет в землю, а мы в это время отнимем как можно большее количество ХП.
Крутить врагов очень весело, особенно доставляет беспомощность какого-то Т34 или ИС-3. Как же так — он танк восьмого уровня и не может ничего сделать несчастной букашке! Хех, такие ситуации просто умиляют:).
Что же, друзья, я почти закончил. Напоследок дам еще один совет — не пользуйтесь автоматическим прицелом! Ни в коем случае! Он неточен до безобразия, поэтому лучше управлять орудием самостоятельно. Это, конечно, иногда отвлекает от вождения, но вы привыкнете, уверяю.!
На этом у меня, пожалуй, все
Обязательно попробуйте это чудо советской инженерной мысли, оно стоит того! И, быть может, именно этот танк станет вашим любимцем не многие-многие сотни боев!
Просто помните — важно выжить до тех пор, пока ситуация станет критической. И тогда вы возьмете свое, обеспечив победу в сражении.
Искренне желаю вам успехов в битвах, еще увидимся!
Расходники и оборудование
После того, как вы приобретете это маленькое советское чудо, вам нужно будет заполнить три слота оборудованием. Что ставить? Обязательно покупаем просветленную оптику, которая добавляет 10% к нашему радиусу обзора. А так как наша задача обнаруживать танки, это оборудование нужно ставить без лишних сомнений. Во второй слот устанавливаем рессоры, которые увеличивают прочность ходовой на 30%. Чрезвычайно полезное оборудование, ведь сбитая гусеница — огромный шанс быть уничтоженным. А так прочность гусениц увеличивается.
Третий слот заполняем на свой вкус, но я предпочитаю возить с собой фильтр «Циклон», увеличивающий прочность двигателя на 50%. Почему именно этот вариант? Все просто — так как мы часто будем оказываться задом к сопернику, выстрел врага может повредить, а то и вовсе остановить двигатель. И снова мы стоим на месте, рискуя быть уничтоженными.
В качестве расходников я советую вам возить с собой ремкомплект для аварийной починки гусениц, аптечку для лечения экипажа и масло, которое добавляет 5% к мощности двигателя. Конечно, 5% это не слишком весомая прибавка, но иногда даже доли секунды играют решающую роль.

Design
The T-50 was an advanced design for its time, with torsion-bar suspension, diesel engine (in common with all the new Soviet tanks) and well-sloped, all-welded armor. An excellent feature was the three-man turret with commander’s cupola, which would not appear on other Soviet tanks until 1942. Most Soviet tanks of the 1939-43 era had either one-man or two-man turrets, which are far less efficient in combat than three-man turrets. Additionally, all T-50s had radios, a feature only found on the commander’s vehicle in earlier models. However, the T-50 had several weaknesses; to begin with, like many Soviet tanks, it was very cramped inside. The main problems, however, were related to the new V-4 engine developed specifically for this tank, unlike other Soviet light AFVs, which used standard truck engines. The T-60 and T-70 light tanks and the SU-76 self-propelled gun used standard GAZ truck engines. Specialized tank engines, more expensive to produce, were reserved for higher-performance AFVs. The very mobile BT-8 fast tank, the T-34 medium tank, KV-1, the IS-2 heavy tanks, and their derivatives all used variants of the same standard 12-cylinder model V-2 diesel engine. The V-4 engine was extremely unreliable, and the design flaws could not be worked out. The engine’s low reliability and high cost contributed to the demise of the T-50.
Development
According to the plan from 1949, the preliminary project was to be approved until 21.8.1949, by the end of 1950 the prototype assembly drawings were supposed to be ready and on 1.3.1950, the first prototype parts production deadline was set. The entire development was to be ready in June 1952.
The VTU oversight of the Škoda project was performed by Maj.Ing. Jan Hajšman and of the ČKD project by Cpt.Ing. Albín Třešňák. During the development, other preliminary projects based on TVP chassis were added, such as the TVP ARV, bridgelayer tank, flame tank and mineclearing TVP with dozer blade. The development of most of these project however was not even started.
Бронирование
У нас нет брони. Абсолютно. Но такова цена за потрясающую мобильность. Да и танк сам по себе принадлежит к легкому классу, поэтому с отсутствием защищенности придется смириться — 37мм брони все-таки…
Впрочем, танк будет радовать вас рикошетами и иногда даже непробитиями. Эх, сколько тем на форуме создано: «не пробил Т-50-2 из БЛ-10, как так??!!!!111111АДЫНАДЫН». А так как сзади танк суживается, вероятность непопаданий возрастает многократно.
Да и вообще в светляка, несущегося со скоростью 70км/час довольно тяжело попасть. А если все же удача противнику улыбнется, у нас будет второй шанс, так как количества ХП хватит на два выстрела большинства врагов.

Combat history
The few T-50s available were deployed on the Leningrad front. Few in-service photos survived and not much is known of their combat record. One uparmored T-50 was captured by Finnish forces and was used by them in 1944. This unit survived the war and is now on display in Finland.On paper, the T-50 should have been easily able to hold its own against any early-war German tank, however, paper specifications cannot always predict real-world performance.
Most light tank production in 1941–43 consisted of the less advanced but simpler T-60 and T-70 light tanks. By 1943, the infantry tank role was considered obsolete, and cheaper SU-76 self-propelled guns took over the light infantry support role. Light tanks in tank regiments were being replaced by T-34 medium tanks. The liaison and reconnaissance roles of light tanks were assumed by cheaper armoured cars and Lend-Leasesupplies of Canadian and British Valentine tanks and U.S. M3 Stuart light tanks.
Variants
There were two variants; a basic model and an up-armored model. Just prior to the German invasion of the USSR, many Soviet tanks had their armor reinforced with welded or bolted add-on plates. Some Kliment Voroshilov heavy tanks, T-28 medium tanks and T-26 light tanks received add-on armor fittings. A few T-50s also received these add-ons. This up-armored variant is recognizable by the bolt heads that hold the armor added to the turret sides and hull front. The normal T-50 is a very ‘clean’ looking vehicle by comparison. Ironically, the armor add-ons were in response to erroneous reports of powerful German antitank and tank guns. The uparmored T-50 had 57 mm of armor at its thickest points.
Surviving vehicles
Modules
Guns
| Gun | Penetration(mm) | Damage(HP) | Rate of fire(rounds/minute) | Dispersion(m/100m) | Aiming time(s) | Weight(kg) |
Price( ) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V | 45 mm VT-43M | 90/130/23 | 70/70/85 | 26.09 | 0.4 | 2 | 312 | 32800 | |
| IV | 45 mm 20KM | 70/95/23 | 47/47/62 | 28.57 | 0.42 | 2.3 | 250 | 20100 |
Turrets
| Turret | Turret Armor (front/sides/rear)(mm) | Turret Traverse Speed(deg/s) | View Range(m) | Weight(kg) |
Price( ) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V | T-50 | 37/37/15 | 48 | 350 | 2000 | 3640 |
| Engine | Engine Power(hp) | Chance of Fire on Impact(%) | Weight(kg) |
Price( ) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IV | V-3 | 300 | 15 | 540 | 4800 | |
| V | V-4M | 400 | 15 | 540 | 15200 |
Suspensions
| Suspension | Load Limit(т) | Traverse Speed(gr/sec) | min | Weight(kg) |
Price( ) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IV | T-50 | 14 | 44 | B/2 | 5000 | 3400 | |
| V | T-50M | 16.1 | 48 | B/2 | 5000 | 9200 |