Танки t-29
Содержание:
Crew
The large cast turret was installed on an 80 inch diameter ring well forward on the hull. The turret armor thickness varied from seven inches on the front to four inches on the rear. A crew of four manned the turret with the tank commander seated under a cupola in the center of the turret-bustle. The gunner was located in the right front of the turret and was provided with a direct-sight telescope in the gun mount and a periscopic sight in the turret roof. The two loaders worked in the rear of the turret ring, one on each side of the cannon. Two hatches, one on each side, were located in the turret roof in addition to the hatch in the commander’s cupola. A circular pistol port was installed in the right side wall of the turret. The 105mm gun T5E1, installed in the combination gun mount T123, was a long-barreled weapon with a muzzle velocity of 3000 feet per second using the 39 pound armor piercing shot (AP) T32. During tests, a 24.6 pound hypervelocity armor piercing shot (HVAP) T29E3 achieved a muzzle velocity of 3700 feet per second. A 33.5 pound T30E1 high explosive shell (HE) was provided with a reduced muzzle velocity of 2500 feet per second. A total of 63 rounds of 105mm ammunition was stowed in the turret and hull. Two .50 caliber machine guns were mounted coaxially on the left side of the 105mm gun. Another .50 caliber machine gun was fitted on a pedestal mount in front of the left loader’s hatch on the turret roof. Ventilation was provided by two 1500cfm blowers. One was mounted in the turret roof to the right rear of the commander’s station, and the other was located in the front hull roof between the driver and the assistant driver.
Комплектация

Вот ветка исследований. Практически все придётся открывать с нуля. Единственное что у нас открыто 100% это предтоповое орудие. Еще возможно открыта радиостанция, но это только в том случае если вы качала арту или ПТ. Давайте рассмотрим модули более подробно:
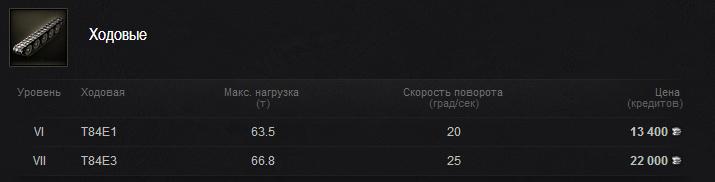
Как и практически на всех машинах, ходовую необходимо открывать как можно быстрее. Она добавит нам проходимости по разным грунтам, скорости поворота и самое главное грузоподъемности. Ставим в первую очередь.
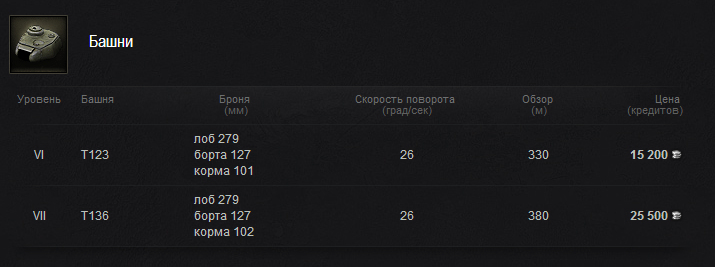
Бронирование обоих башен просто феноменальное, конечно есть уязвимые места, но картины они не портят. Все-таки БЛ-10 не каждый раз попадает в командирский люк =)
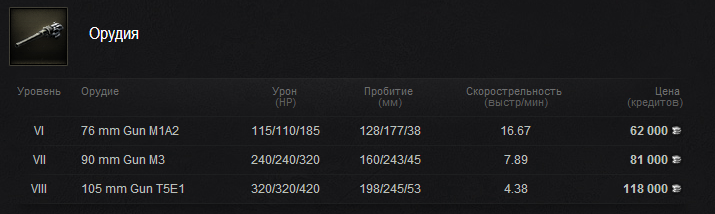
Предтоповое орудие у нас должно быть открыто. После установки ходовой и башни сразу копим опыт на топ. орудие. С ним играть комфортно: показатели бронепробития достаточно хорошие, скорострельность и урон тоже на уровне, а вот с точностью беда, но беда относительная.
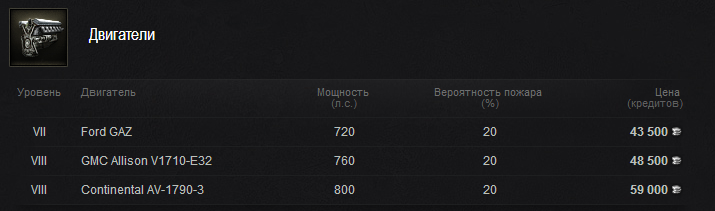
Двигатели нам особой прибавки не дают. Я например, прокачивая Т29 открыл все топ модули за свободный опыт кроме двигателей. Хоть они и идут на Т32, открывать их сразу сломя голову не нужно. Двигатели как двигатели, ничего особенного. Только на мой взгляд ценна за них завышена.
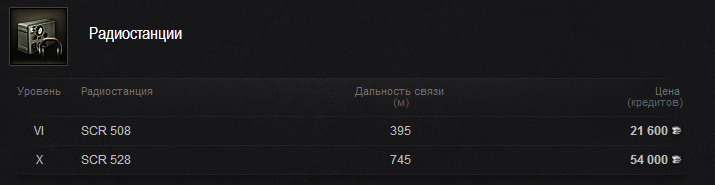
Радиостанция у нас более чем хорошая. Нам ее хватит за глаза. Топовые ТТ имеют 750 м, а у нас 745 м. Радиостанция важна для результативной игры. Нам нужно знать что происходит на другом фланге. Где нужна наша помощь и т. д.
В целом выделю такие достоинства и недостатки
Плюсы
- Феноменальное бронирование башни
- Хорошее пробитие орудия
- Комфортность игры
- Хорошие углы наводки
Минусы
- Слабое бронирование корпуса
- Орудие иногда показывает чудеса в плане точности
Балансный вес

Мы попадаем на 7 – 9 уровни боев, играть комфортно везде. С 9 уровнем конечно играть будет не совсем приятно, но терпимо. На 7 – 8 пробивать мы будем всех и стабильно наносить урон.
Прибыльность
На 7 уровне с ПА вы будете достаточно хорошо фармить. Конечно стоимость снарядов теперь увеличится в несколько раз, но это не критично для владельцем ПА. Тем кто играет без ПА необходимо иметь фарм машину. Играть без ПА в ноль можно, но вот фармить получиться лишь при стабильно хорошей игре …
Тактика
Мы достаточно интересное ТТ. Танковать броней нам нельзя т. к. в корпусе ее нет, а в башню будут стрелять только самые недалекие люди. На Т29 можно занимать позиции когда видна только башня, в складках местности или за подбитыми танками. Такая позиция будет иметь кучу достоинств и один огромный минус – арта. Если занять позицию в месте где арта крыть не будет то будет все прекрасно. Лично когда я занимал такую позицию, об меня одного + пару танков мог разбиться целый раш. Я неоднократно говорил, что главное при игре на абсолютно любой технике – думать. Думайте и понимайте что делаете и все будет хорошо.
Crew
The large cast turret was installed on an 80 inch diameter ring well forward on the hull. The turret armor thickness varied from seven inches on the front to four inches on the rear. A crew of four manned the turret with the tank commander seated under a cupola in the center of the turret-bustle. The gunner was located in the right front of the turret and was provided with a direct-sight telescope in the gun mount and a periscopic sight in the turret roof. The two loaders worked in the rear of the turret ring, one on each side of the cannon. Two hatches, one on each side, were located in the turret roof in addition to the hatch in the commander’s cupola. A circular pistol port was installed in the right side wall of the turret. The 105mm gun T5E1, installed in the combination gun mount T123, was a long-barreled weapon with a muzzle velocity of 3000 feet per second using the 39 pound armor piercing shot (AP) T32. During tests, a 24.6 pound hypervelocity armor piercing shot (HVAP) T29E3 achieved a muzzle velocity of 3700 feet per second. A 33.5 pound T30E1 high explosive shell (HE) was provided with a reduced muzzle velocity of 2500 feet per second. A total of 63 rounds of 105mm ammunition was stowed in the turret and hull. Two .50 caliber machine guns were mounted coaxially on the left side of the 105mm gun. Another .50 caliber machine gun was fitted on a pedestal mount in front of the left loader’s hatch on the turret roof. Ventilation was provided by two 1500cfm blowers. One was mounted in the turret roof to the right rear of the commander’s station, and the other was located in the front hull roof between the driver and the assistant driver.
Ссылки
- В сети Интернет
Википедия
Техника США
| Лёгкие танки | I T1 Cunningham • II M2 Light Tank • II T1E6 • II T2 Light Tank • II T7 Combat Car • III M22 Locust • III M3 Stuart • III MTLS-1G14 • IV M5 Stuart • V M24 Chaffee • V M7 • VI T21 • VI T37 • VII T71 CMCD • VII T71 DA • VIII T92 • VIII M41 Walker Bulldog • IX T49 • X XM551 Sheridan |
| Средние танки | II T2 Medium Tank • III M2 Medium Tank • IV T6 Medium • IV M3 Lee • V M4 Improved • V M4A2E4 Sherman • V M4A1 Sherman • V Ram II • VI M4A3E8 Fury • VI M4A3E8 Thunderbolt VII • VI M4A3E8 Sherman • VI M4A3E2 Sherman Jumbo • VII T26E3 Eagle 7 • VII T20 • VII T23E3 • VIII T25 Pilot Number 1 • VIII TL-1 LPC • VIII M46 Patton KR • VIII M26 Pershing • VIII T26E4 SuperPershing • VIII T26E4 SuperPershing FL • VIII T69 • VIII T95E2 • IX M46 Patton • X M48A5 Patton • X M60 • X T95E6 |
| Тяжёлые танки | V T14 • V T1 Heavy Tank • VI M6 • VII King Tiger (захваченный) • VII T29 • VIII Chrysler K • VIII Chrysler K GF • VIII T26E5 • VIII T26E5 Patriot • VIII M54 Renegade • VIII M6A2E1 • VIII T32 • VIII T34 • VIII T34 B • IX AE Phase I • IX M103 • IX T54E1 • X T110E5 • X T57 Heavy Tank |
| ПТ-САУ | II T3 HMC • III T56 GMC • IV M8A1 • IV T40 • V M10 Wolverine • V T67 • VI T78 • VI M18 Hellcat • VI M36 Jackson • VII M56 Scorpion • VII T28 Concept • VII Super Hellcat • VII T25/2 • VII T25 AT • VIII TS-5 • VIII T28 • VIII T28 Prototype • IX T30 • IX T95 • X T110E3 • X T110E4 |
| САУ | II T1 HMC • III T18 HMC • III M7 Priest • IV T82 HMC • IV M37 • V M41 HMC • VI M44 • VII M12 • VIII M40/M43 • IX M53/M55 • X T92 HMC |
Средние танки
| Техника СССР | III Т-29 • IV А-32 • IV Т-28Э с Ф-30 • IV Т-28 • V Матильда IV • V Т-34 экранированный • V Т-34 • VI А-43 • VI Т-34-85М • VI Т-34-85 Rudy • VI М4-А2 Шерман Лозы • VI Т-34-85 • VII А-44 • VII КВ-13 • VII Т-43 • VIII Объект 416 • VIII Т-54 первый образец • VIII Т-44-100 (Б) • VIII Т-44-100 (К) • VIII Т-44-100 (Р) • VIII Т-44-100 (У) • VIII СТГ • VIII СТГ Гвардеец • VIII Т-44 • IX Объект 430 Вариант II • IX Объект 430 • IX Т-54 • X Объект 140 • X Объект 907 • X Т-22 ср. • X К-91 • X Объект 430У • X Т-62А |
| Техника Германии | III Großtraktor — Krupp • III Pz.Kpfw. IV Ausf. A • III Pz.Kpfw. S35 739 (f) • IV Pz.Kpfw. III Ausf. J • IV Pz.Kpfw. IV Ausf. D • IV VK 20.01 (D) • V Pz.Kpfw. III Ausf. K • V Turán III prototípus • V Pz.Kpfw. III/IV • V Pz.Kpfw. IV hydrostat. • V Pz.Kpfw. V/IV • V Pz.Kpfw. V/IV Alpha • V Pz.Kpfw. IV Ausf. H • V Pz.Kpfw. T 25 • V VK 30.01 (H) • VI Pz.Kpfw. IV Schmalturm • VI VK 30.01 (D) • VI VK 30.02 (M) • VII Panther/M10 • VII Panther • VII VK 30.02 (D) • VIII Panther mit 8,8 cm L/71 • VIII Panzer 58 • VIII Schwarzpanzer 58 • VIII Panzer 58 Mutz • VIII M48A2 Räumpanzer • VIII Indien-Panzer • VIII Panther II • IX E 50 • IX T 55A • IX Kampfpanzer 50 t • IX Leopard Prototyp A • X E 50 Ausf. M • X Leopard 1 |
| Техника США | II T2 Medium Tank • III M2 Medium Tank • IV T6 Medium • IV M3 Lee • V M4 Improved • V M4A2E4 Sherman • V M4A1 Sherman • V Ram II • VI M4A3E8 Fury • VI M4A3E8 Thunderbolt VII • VI M4A3E8 Sherman • VI M4A3E2 Sherman Jumbo • VII T26E3 Eagle 7 • VII T20 • VII T23E3 • VIII T25 Pilot Number 1 • VIII TL-1 LPC • VIII M46 Patton KR • VIII M26 Pershing • VIII T26E4 SuperPershing • VIII T26E4 SuperPershing FL • VIII T69 • VIII T95E2 • IX M46 Patton • X M48A5 Patton • X M60 • X T95E6 |
| Техника Франции | III D2 • III Somua S35 • IV SARL 42 • V Renault G1 • VI Bretagne Panther • VIII Bat.-Châtillon Bourrasque • VIII Lorraine 40 t • VIII AMX Chasseur de chars • VIII M4A1 Revalorisé • IX AMX 30 1er prototype • IX Char Futur 4 • IX Bat.-Châtillon 25 t AP • X Bat.-Châtillon 25 t • X AMX 30 B |
| Техника Великобритании | I Vickers Medium Mk. I • II Vickers Medium Mk. II • III Vickers Medium Mk. III • IV Matilda • IV Grant • IV AC 1 Sentinel • V Cavalier • V Sherman III • V Matilda Black Prince • VI Sherman Firefly • VI Cromwell • VI AC 4 Experimental • VI Cromwell B • VI Sherman VC Firefly • VII Comet • VIII Centurion Mk. I • VIII FV4202 • VIII Chieftain/T95 • VIII Centurion Mk. 5/1 RAAC • VIII Chimera • IX Centurion Mk. 7/1 • X Centurion Action X |
| Техника Китая | V Type T-34 • VI Type 58 • VII T-34-1 • VIII Type 59 • VIII T-34-2 • VIII T-34-3 • VIII 59-Patton • VIII Type 59 G • IX WZ-120 • X • X 121B |
| Техника Японии | II Chi-Ni • II Type 89 I-Go/Chi-Ro • IV Type 1 Chi-He • V Type 3 Chi-Nu • V Type 3 Chi-Nu Kai • VI Type 4 Chi-To • VII Type 5 Chi-Ri • VIII STA-1 • VIII STA-2 • IX Type 61 • X STB-1 |
| Техника Чехословакии | IV ST vz. 39 • V Škoda T 24 • VI Škoda T 40 • VI Škoda T 25 • VII Konštrukta T-34/100 • VIII TVP VTU Koncept • VIII Škoda T 27 • IX Škoda T 50 • X TVP T 50/51 |
| Техника Швеции | IV Lago • V Strv m/42 • VI Strv m/42-57 Alt A.2 • VI Strv 74 • VII Leo • VIII Strv 81 • VIII Primo Victoria • VIII Lansen C • VIII UDES 14 Alt 5 • IX UDES 16 • X UDES 15/16 |
| Техника Польша | V 25TP KSUST II • VI Pudel • VI 40TP Habicha • VI T-34-85 Rudy |
| Техника Италии | II M14/41 • III M15/42 • IV P26/40 • V P.43 • VI P.43 bis • VII P.43 ter • VIII Progetto M35 mod. 46 • VIII P.44 Pantera • IX Prototipo Standard B • X Progetto M40 mod. 65 |
T-series prototypes
The T29, T30, T32, and T34 series of tanks were used to evaluate numerous experimental components after World War II. Although too late for the war for which they were designed, they provided invaluable service in developing these components for later tanks. Much of the work which made the early AV-1790 engine and the CD-850 transmission a reliable power package utilized these tanks. Later, they were used in the development of other power train components such as the XT-1400 transmission, which was tested in the T30.
| Mk.VII | M6 | T28 | T29 | T30 | T32 | T34 | M103A2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crew | 8 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 5 |
| Length | 10,43m | 8,43m | 11,12m | 11,56m | 10,9m | 10,83m | 11,77m | 11,23m |
| Width | 3,66m | 3,12m | 4,54m | 3,8m | 3,8m | 3,76m | 3,8m | 3,63m |
| Height | 3,12m | 3,00m | 2,86m | 3,22m | 3,22m | 2,81m | 3,22m | 3,56m |
| Weight | 39,5t | 57,4t | 86,3t | 64,25t | 64,74t | 54,5t | 65,2t | 58,1t |
| Enginepower | Liberty338hp | G-200960hp | GAF500hp | GAC770hp | AV1790810hp | GAC770hp | AV1790810hp | AV1790750hp |
| Max. speed | 8,8km/h | 35km/h | 12,8km/h | 35km/h | 35km/h | 35km/h | 35km/h | 37km/h |
| hull armour(angle) | 12mm(28) | 83mm(30) | 305mm | 102mm(54) | 102mm(54) | 127mm(54) | 102mm(54) | 127mm(60) |
| side armour | 12mm | 70mm | 152mm | 76mm | 76mm | 76mm | 76mm | 51mm |
| Turret armour(mantlet) | 16mm | 83mm(102mm) | — | 178mm(279mm) | 178mm(279mm) | 298mm(298mm) | 178mm(279mm) | 127mm(254mm) |
| top armour | 6-10mm | 25mm | 38mm | 38mm | 38mm | 38mm | 38mm | 38mm |
| bottom armour | 6-8mm | 25mm | 25mm | 25mm | 25mm | 25mm | 25mm | 38mm |
| Gun | 2x57mmHotchkiss | 75mm M737mm MB | 105mmT5E1 | 105mmT5E2 | 155mmT7 | 90mmT15E2 | 120mmT53 | 120mmM58 |
| Secondaryarmament | 5×7,62mmHotchkiss | 2×12,7mm HB M22x7,62mmM1919A4 | 12,7mmHB M2 | 3×12,7mmHB M27.62mmM1919M4 | 2×12,7mmHB M27.62mmM1919M4 | 12,7mmHB M22x7.62mmM1919M4 | 3×12,7mmHB M27.62mmM1919M4 | 3×12,7mmHB M27.62mmM37 |
History
An order for the T29 tank was approved on 12 April 1945, but the numbers were reduced to 1152. Also in April, four additional prototype T29s were authorized, but later, it was directed that one of these was to be armed with the 120mm gun T53 and redesignated as the heavy tank T34. This was only one of the many changes to the program with the approaching end of hostilities. After the end of the war in the Pacific, the production contract with the Pressed Steel Car Company, Inc. was terminated with one T29 completed and a second partially finished. All material was transferred to Detroit Arsenal for the completion of ten prototypes for postwar development studies authorized on 23 August, 1945. Later, the total of T29 prototypes was reduced to eight.
T-series prototypes
The T29, T30, T32, and T34 series of tanks were used to evaluate numerous experimental components after World War II. Although too late for the war for which they were designed, they provided invaluable service in developing these components for later tanks. Much of the work which made the early AV-1790 engine and the CD-850 transmission a reliable power package utilized these tanks. Later, they were used in the development of other power train components such as the XT-1400 transmission, which was tested in the T30.
| Mk.VII | M6 | T28 | T29 | T30 | T32 | T34 | M103A2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crew | 8 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 5 |
| Length | 10,43m | 8,43m | 11,12m | 11,56m | 10,9m | 10,83m | 11,77m | 11,23m |
| Width | 3,66m | 3,12m | 4,54m | 3,8m | 3,8m | 3,76m | 3,8m | 3,63m |
| Height | 3,12m | 3,00m | 2,86m | 3,22m | 3,22m | 2,81m | 3,22m | 3,56m |
| Weight | 39,5t | 57,4t | 86,3t | 64,25t | 64,74t | 54,5t | 65,2t | 58,1t |
| Enginepower | Liberty338hp | G-200960hp | GAF500hp | GAC770hp | AV1790810hp | GAC770hp | AV1790810hp | AV1790750hp |
| Max. speed | 8,8km/h | 35km/h | 12,8km/h | 35km/h | 35km/h | 35km/h | 35km/h | 37km/h |
| hull armour(angle) | 12mm(28) | 83mm(30) | 305mm | 102mm(54) | 102mm(54) | 127mm(54) | 102mm(54) | 127mm(60) |
| side armour | 12mm | 70mm | 152mm | 76mm | 76mm | 76mm | 76mm | 51mm |
| Turret armour(mantlet) | 16mm | 83mm(102mm) | — | 178mm(279mm) | 178mm(279mm) | 298mm(298mm) | 178mm(279mm) | 127mm(254mm) |
| top armour | 6-10mm | 25mm | 38mm | 38mm | 38mm | 38mm | 38mm | 38mm |
| bottom armour | 6-8mm | 25mm | 25mm | 25mm | 25mm | 25mm | 25mm | 38mm |
| Gun | 2x57mmHotchkiss | 75mm M737mm MB | 105mmT5E1 | 105mmT5E2 | 155mmT7 | 90mmT15E2 | 120mmT53 | 120mmM58 |
| Secondaryarmament | 5×7,62mmHotchkiss | 2×12,7mm HB M22x7,62mmM1919A4 | 12,7mmHB M2 | 3×12,7mmHB M27.62mmM1919M4 | 2×12,7mmHB M27.62mmM1919M4 | 12,7mmHB M22x7.62mmM1919M4 | 3×12,7mmHB M27.62mmM1919M4 | 3×12,7mmHB M27.62mmM37 |
Эксплуатация и боевое применение
Достоверных сведений о боевом применении трёх изготовленных образцов Т-29 нет.
Т-29-4 был передан на полигон в Кубинке, где находился до начала Великой Отечественной войны. Осенью 1941 года он был передан в состав 22-й танковой бригады. Что было с ним потом, неизвестно.
Т-29-5 был разобран в 1938 году.
Эталонный Т-29 в том же году был перевооружён пушкой Л-10. После начала советско-финской войны этот танк был отремонтирован и 13 февраля 1940 года «убыл в распоряжение АБТВ 13-й армии». Однако о боевом применении танка ничего не известно, равно как и о его дальнейшей судьбе.
Как минимум один из Т-29 был эвакуирован в Челябинск, и по состоянию 1942 год находился на территории опытного завода № 100. Согласно документам, в конце 1943 года эта машина была пущена в переплавку вместе с Т-100, КВ-7 и рядом других опытных образцов бронетехники.
History
Development
Projects for a dedicated heavy tank for the U.S. Armed Forces began in March 1944 as a response to the German heavy tanks that have been popping up in Europe. While the T26E3 tank, later known as the M26 Pershing was slated to be the next-generation American tank, it was still considered unsuitable against the even heavier Tiger II. A project to increase the armour and firepower commenced countering this problem, the project titled Heavy Tank T29. Using design elements from the T26E3 with thicker armour and lengthened hull, the T29 also was equipped with the 105 mm Gun T5, a gun in development alongside the heavy assault tank T95. Other features included a 770 hp Ford GAC engine, armour thickness up to 279 mm effective, and a coincidence range-finder. The heavy armour and armament made the tank weigh about 64 tons, making it a close match to the Tiger II.
Though the T29 was monstrous itself, side projects involving the T29 crafted the T30 Heavy Tank. Itself similar to the T29 in terms of armour, but featured a monstrous 155 mm Gun T7 with a more powerful engine and an extra crew member to facilitate loading the gun.
Effect in World War II
Throughout World War II, the T29 and the T30 stayed in development under the priority «limited procurement». Eventually, the war in Europe ended in May 1945, but the small ordered stayed in hope it may be useful in the Japan invasion in Operation Downfall. That hope was smashed as well when Japan surrendered in September 1945, ending World War II. Even if an operation commenced that used these vehicles, the Army Ground Forces objected to the use of such heavy equipment due to the lack of adequate transporters. Further production was cancelled in the post-war demilitarization.
Post World War Effect
The heavy tank concept didn’t end with the war and a final attempt was made to remake the T29 into a more modern, lethal weapon system. This produced the T34 Heavy Tank, which mounted a 120 mm gun based on the M1 anti-aircraft gun. The calibre made an adequate balance of firepower and loading ease between the 105 mm and the 155 mm used in the T29 and T30. In fact, the two T34 pilot models made were a converted T29 and T30. However, the demilitarization took down the T34 program as well, but the experience in this project help engineers in the development of the M103 Heavy Tank.
Today, there are a few T29s still in display across the United States, most of them residing in storage at Fort Benning, Georgia where they will be used as a display in the future National Armor and Cavalry Museum.
History
An order for the T29 tank was approved on 12 April 1945, but the numbers were reduced to 1152. Also in April, four additional prototype T29s were authorized, but later, it was directed that one of these was to be armed with the 120mm gun T53 and redesignated as the heavy tank T34. This was only one of the many changes to the program with the approaching end of hostilities. After the end of the war in the Pacific, the production contract with the Pressed Steel Car Company, Inc. was terminated with one T29 completed and a second partially finished. All material was transferred to Detroit Arsenal for the completion of ten prototypes for postwar development studies authorized on 23 August, 1945. Later, the total of T29 prototypes was reduced to eight.
Usage in battles
Some specific enemies to worry about:
- Tiger II (P) and (H): These are going to be the most common and equal enemy in the T29. While most of the T29’s front armour can take on the 88 mm APCBC round, APCR can penetrate the front mantlet of the turret. It can also aim for the lower glacis on the hull, which will knock-out the driver and can repeatedly do this until the entire crew gets knocked out. To fight the Tiger II’s, aim at the «cheeks» of the turret with any ammo, preferably the right as that is where the gunner sits. Using the T32 APBC ammo, there is a chance that it can penetrate the Tiger II’s front glacis at close range (less than 100 meters) and the lower glacis from even further, making the T32 round probably the most preferable round to use against the Tiger II’s front. If the T29 can get the Tiger’s side though, a simple T13 APCBC round can turn a Tiger II into a fiery ball of fire.
- Tiger II 10.5 cm: Though the same rule applies to the 88 mm Tiger II, take extreme caution as the 10.5 cm cannon can devastate the T29’s interior if it penetrates, and it can from the front.
- Jagdpanther: Equipped with the same 88 as on the Tiger II, this TD can do some damage if it can get a good shot off the T29. However, the T29’s 105 mm cannon can easily penetrate through its front glacis, just don’t shoot too close to the gun or the gun mantlet may bounce it.
- Ferdinand: The greater armour on this tank destroyer makes it harder to fight in a long-range engagement. However, if the T29 can get closer, the flat armour space on the top superstructure and the hull front can prove more vulnerable. Of course, getting to the side of this tank destroyer is a guaranteed point if an APCBC round can be landed into it.
- SU/ISU-152: While easily destroyed by one shot of the 105 mm cannon, the 152 mm howitzer still can do unspeakable damage if it hits the T29’s vulnerable turret and hull roof.
Modules
| Tier | Mobility | Protection | Firepower | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Tracks | Parts | Horizontal Drive | T13 | |
| II | Suspension | Brake System | FPE | Adjustment of Fire | T29E3 |
| III | Filters | Crew Replenishment | Elevation Mechanism | ||
| IV | Transmission | Engine | |||
| This is a premium vehicle: all modifications are unlocked on purchase |
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Extremely good 105 mm gun, arguably the best gun at Rank 4
- T13 round has great penetration values with a substantial amount of TNT packed inside; can help players easily one-shot opponents with its post-penetration damage
- An Ace crew will reload the gun every 12.5 seconds — very fast for the firepower
- APCR shells can go through the Jagdtiger’s superstructure
- Great overall armour layout — the front and sides of the hull and turret are very well armoured
- 10 degrees of gun depression makes the vehicle great at hull down fighting
- Reasonable top speed and maneuverability
- Can carry a substantial amount of ammo for prolonged combat
- Armed with three .50 caliber machine guns, allowing the vehicle to shred through lightly armoured vehicles, vehicle modules like tracks, and low-flying aircraft
- One of the best pound-for-pound tanks in the game
Cons:
- Enemy will highlight the T29 as a priority target, attracting lots of enemy attention
- Gun mantlet is not impenetrable, with the common opponent (Tiger II) able to punch through it at ranges excess of 500 meters
- Massive tank that is easily visible even from the air and is hard to hide from being spotted
- Sides of the engine compartment isn’t as tough as the sides of the hull.
- Only one .50 caliber machine gun can effectively engage aircraft flying higher than coaxial level
- Mediocre shell velocity for the T13 APHE shell
- Despite the default APCBC shell having no explosive filler, it has the same penetration values as the T13 shell and so offers no advantages whatsoever if brought into a battle
Models
T29E2 Prototype
T29T29s
T29 number 1 was diverted to General Motors Corporation for the installation of a modified version of the Allison liquid-cooled V-12 aircraft engine. To accommodate the new power package consisting of the Allison V-1710-E32 engine and the CD-850-1 cross-drive transmission, the tank hull was lengthened by 1 31/32 inches. The new engine developed 870 gross horsepower at 2800 rpm and weighed about 1600 pounds dry. This vehicle, armed with the 105mm gun T5EI in mount T123, was designated as the heavy tank T29E1 in December 1945.
T29 number 2 was fitted with what was designated as the heavy tank turret T5. This turret was equipped with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology combination hydraulic power turret traversing and elevating mechanism and computing sight.
The tank was armed with the 105mm gun T5E2 in mount T123E2. OCM 32107, dated I April 1948, designated the T29 with the T5 turret as the heavy tank T29E2.
At this point, a brief description of the guns and mounts is in order. The 105mm gun T5E1 was installed in mount T123, which used three recoil cylinders on top of the gun cradle. This design was modified to have two recoil cylinders on top of the cradle and one on the bottom. This new mount was the T123E1 and the cannon modified to fit it was the 105mm gun T5E2. Installation of the power traversing and elevating system in the T29E2 tank required further modification of the mount, and it received the new designation T123E2. Heavy tanks T29 numbers 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 were all armed with the 105mm gun T5E2 in mount T123E1.
T29
T29E3 Prototype
T29
Description

The Heavy Tank T29 is a gift rank IV American heavy tank
with a battle rating of 7.0 (AB/RB) and 6.7 (SB). The T29 was introduced in the Update 1.59 «Flaming Arrows» as a gift vehicle and was available on the Gaijin store for pre-order before the update. The T29 is a formidable heavy tank that introduces the 105 mm T5 cannon in a rotating turret rather than in the fixed case-mate setting on the T95, with a tougher-than-average gun mantlet, and a sloped, but slightly thin hull.
The T29 is perhaps one of the most formidable heavy tanks at Rank IV, right up there with the IS-2 and Tiger IIs. With the 105 mm cannon, the T29 can engage most enemies it faces on the battlefield from the front, often destroying an enemy tank with a single shot with the extremely powerful T13 APCBC rounds, and with armour thick enough to block most incoming rounds. The T29 can act as the «damage sponge» of the team by directing most of the enemy fire towards it. It can also act as a sniping tank by setting it in the back or sides and fire at any unsuspecting enemy tank. A simple APCBC round can destroy even the strongest tank if it penetrates the side armour. Another useful advantage is that the tank is well rounded, but is directed to being a heavy tank in arcade battles, making it especially powerful. It has average mobility for the heavy tank class but has a lower top speed than it’s main rivals, the IS-2 mod. 1944 and the Tiger IIs, better than only that the Caernarvon. However, it possesses above average acceleration, making it more suited for dense environments. It’s gun also possesses a high muzzle velocity, making sniping a viable option.
History
An order for the T29 tank was approved on 12 April 1945, but the numbers were reduced to 1152. Also in April, four additional prototype T29s were authorized, but later, it was directed that one of these was to be armed with the 120mm gun T53 and redesignated as the heavy tank T34. This was only one of the many changes to the program with the approaching end of hostilities. After the end of the war in the Pacific, the production contract with the Pressed Steel Car Company, Inc. was terminated with one T29 completed and a second partially finished. All material was transferred to Detroit Arsenal for the completion of ten prototypes for postwar development studies authorized on 23 August, 1945. Later, the total of T29 prototypes was reduced to eight.
T-series prototypes
The T29, T30, T32, and T34 series of tanks were used to evaluate numerous experimental components after World War II. Although too late for the war for which they were designed, they provided invaluable service in developing these components for later tanks. Much of the work which made the early AV-1790 engine and the CD-850 transmission a reliable power package utilized these tanks. Later, they were used in the development of other power train components such as the XT-1400 transmission, which was tested in the T30.
| Mk.VII | M6 | T28 | T29 | T30 | T32 | T34 | M103A2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crew | 8 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 5 |
| Length | 10,43m | 8,43m | 11,12m | 11,56m | 10,9m | 10,83m | 11,77m | 11,23m |
| Width | 3,66m | 3,12m | 4,54m | 3,8m | 3,8m | 3,76m | 3,8m | 3,63m |
| Height | 3,12m | 3,00m | 2,86m | 3,22m | 3,22m | 2,81m | 3,22m | 3,56m |
| Weight | 39,5t | 57,4t | 86,3t | 64,25t | 64,74t | 54,5t | 65,2t | 58,1t |
| Enginepower | Liberty338hp | G-200960hp | GAF500hp | GAC770hp | AV1790810hp | GAC770hp | AV1790810hp | AV1790750hp |
| Max. speed | 8,8km/h | 35km/h | 12,8km/h | 35km/h | 35km/h | 35km/h | 35km/h | 37km/h |
| hull armour(angle) | 12mm(28) | 83mm(30) | 305mm | 102mm(54) | 102mm(54) | 127mm(54) | 102mm(54) | 127mm(60) |
| side armour | 12mm | 70mm | 152mm | 76mm | 76mm | 76mm | 76mm | 51mm |
| Turret armour(mantlet) | 16mm | 83mm(102mm) | — | 178mm(279mm) | 178mm(279mm) | 298mm(298mm) | 178mm(279mm) | 127mm(254mm) |
| top armour | 6-10mm | 25mm | 38mm | 38mm | 38mm | 38mm | 38mm | 38mm |
| bottom armour | 6-8mm | 25mm | 25mm | 25mm | 25mm | 25mm | 25mm | 38mm |
| Gun | 2x57mmHotchkiss | 75mm M737mm MB | 105mmT5E1 | 105mmT5E2 | 155mmT7 | 90mmT15E2 | 120mmT53 | 120mmM58 |
| Secondaryarmament | 5×7,62mmHotchkiss | 2×12,7mm HB M22x7,62mmM1919A4 | 12,7mmHB M2 | 3×12,7mmHB M27.62mmM1919M4 | 2×12,7mmHB M27.62mmM1919M4 | 12,7mmHB M22x7.62mmM1919M4 | 3×12,7mmHB M27.62mmM1919M4 | 3×12,7mmHB M27.62mmM37 |
Armaments
Main armament
Main article: T5E2 (105 mm)
| 105 mm T5E2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capacity | Vertical guidance | Horizontal guidance | |||
| 63 | -10°/+15° | ±180° | |||
| Turret rotation speed (°/s) | |||||
| Mode | Stock | Upgraded | Prior + Full crew | Prior + Expert qualif. | Prior + Ace qualif. |
| Arcade | 10.71 | 14.80 | 18.00 | 19.90 | 21.20 |
| Realistic | 10.71 | 12.60 | 15.30 | 16.90 | 18.00 |
| Reloading rate (seconds) | |||||
| Stock | Prior + Full crew | Prior + Expert qualif. | Prior + Ace qualif. | ||
| 16.25 | 14.38 | 13.25 | 12.50 |
Ammunition
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead | Penetration in mm @ 0° Angle of Attack | |||||
| 10m | 100m | 500m | 1000m | 1500m | 2000m | ||
| T32 | APCBC | 256 | 253 | 238 | 221 | 205 | 190 |
| T13 | APCBC | 253 | 250 | 236 | 219 | 204 | 190 |
| T29E3 | APCR | 292 | 287 | 266 | 242 | 220 | 200 |
| T30E1 | HE | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Shell details | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Velocity in m/s | ProjectileMass in kg | Fuse delay
in m: |
Fuse sensitivity
in mm: |
Explosive Mass in g (TNT equivalent): | Normalization At 30° from horizontal: | Ricochet: | ||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | |||||||
| T32 | 914 | 17.7 | N/A | N/A | N/A | +4° | 48° | 63° | 71° |
| T13 | 899 | 18.59 | 1.2 | 19 | 177.38 | +4° | 48° | 63° | 71° |
| T29E3 | 1128 | 11.2 | N/A | N/A | N/A | +1.5° | 66° | 70° | 72° |
| T30E1 | 945 | 15.2 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1,550 | +0° | 79° | 80° | 81° |
Ammo racks
| Full ammo | AmmoPart | 1st rack empty | 2nd rack empty | 3rd rack empty | 4th rack empty | 5th rack empty | 6th rack empty | 7th rack empty | 8th rack empty | 9th rack empty | Visual discrepancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 63 | ProjectilesPropellants | 62 (+1)62 (+1) | 56 (+7)56 (+7) | 48 (+15)48 (+15) | 41 (+22)41 (+22) | 34 (+29)34 (+29) | 27 (+36)27 (+36) | 17 (+46)17 (+46) | 7 (+56)7 (+56) | 1 (+62)1 (+62) | no |
| 12.7 mm M2HB | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pintle mount | |||
| Capacity (Belt capacity) | Fire rate (shots/minute) | Vertical guidance | Horizontal guidance |
| 1,000 (200) | 576 | -10°/+50° | ±120° |
| Coaxial mount #1 | |||
| Capacity (Belt capacity) | Fire rate (shots/minute) | Vertical guidance | Horizontal guidance |
| 1,200 (200) | 576 | N/A | N/A |
| Coaxial mount #2 | |||
| Capacity (Belt capacity) | Fire rate (shots/minute) | Vertical guidance | Horizontal guidance |
| 1,200 (200) | 576 | N/A | N/A |
Историческая справка
-
Основная статья: История T20
T20 (англ. Medium Tank T20) — серия опытных средних танков, созданных в США в период Второй мировой войны. Программа по созданию нового среднего танка, превосходящего германские аналоги, предназначенного для замены M4, была начата в 1942 году. В мае—июне 1943 года были последовательно построены два прототипа танка T20 и два прототипа его усовершенствованного варианта, T22. Хотя испытания T20 и T22 продолжались вплоть до 1944 года, танки были сочтены не соответствующими требованиям армии. Кроме этого в 1943 году были разработан танк T23, оснащённый электромеханической трансмиссией. После успешных испытаний, было принято решение о серийном производстве T23, но после дальнейших испытаний танк был отвергнут армией и его производство ограничилось опытной партией из 10 серийных машин.
На танках серии T20 был испытан ряд технических новшеств, некоторые из которых в дальнейшем были внедрены в серийных танках; в частности, T22E1 стал первым в мире танком, оснащённым автоматом заряжания. Дальнейшее развитие серии T20 в 1943—1944 годах, в виде танков T25 и T26, привело к созданию танка M26, запущенного в серийное производство в ноябре 1944 года и в ограниченных масштабах использовавшегося в боях в Западной Европе весной 1945 года.
История создания
Одной из характерных особенностей советского (и не только) танкостроения 1930-х годов являлась большая работа по разработке и созданию колёсно-гусеничных танков. Применение колёсно-гусеничного движителя сильно усложняло силовую передачу и ходовую часть танков, однако давало явный выигрыш в скорости. Кроме того, таким образом решалась проблема низкого ресурса гусениц, не позволявшего танкам тех лет совершать длительные марши. Наконец, предполагалось, что в случае повреждения гусеничного движителя экипаж будет просто сбрасывать разбитую гусеницу, пусть теряя в проходимости танка, но сохраняя его подвижность.
В программе развития автобронетанковых войск РККА колёсно-гусеничные танки занимали существенное место. Предполагалось, помимо имевшихся в наличии лёгких танков серии БТ, разработать также средний танк с колёсно-гусеничным движителем.
Разработка среднего колёсно-гусеничного танка в СССР началась в 1933 году с подготовки Автобронетанковым бюро техотдела ЭКУ ОГПУ ряда эскизных проектов танков, представлявших собой дальнейшее развитие танка БТ-2 и во многом опиравшихся на разработанный недавно танк Т-28. Основной из них, носивший условное обозначение ПТ-1, имел привод на три пары опорных катков (при движении на гусеницах), а также обладал способностью плавать. Также было разработано пять полностью «сухопутных» вариантов танка, из которых наибольший интерес среди военных вызвали 4-й и 5-й проекты под общим названием ИТ-3 («истребительный танк, третий»). Машина имела массу 17—20 т (в зависимости от бронирования), защищалась противопульной бронёй и вооружалась 76-мм орудием и пулемётами калибра 7,62 и 12,7 мм. Двигатель М-17Б мощностью 500 л.с. должен был разгонять машину до 60 км/ч на гусеницах и 80 км/ч — на колёсах. Экипаж составлял 4 человека. В 1934 году, после доработки этих двух проектов, на ленинградском Кировском заводе, где в то время разворачивался выпуск Т-28, были построены опытные танки Т-29-4 и Т-29-5. Проект разрабатывался под общим руководством Н. В. Цейца, непосредственное участие в разработке танка принимал Н. А. Астров. Между собой танки различались бронированием (15—20 или 20—33 мм соответственно), массой (16 или 23,5 т) и рядом других параметров. По компоновке и вооружению танки были одинаковы и соответствовали Т-28.
В 1934—1935 годах танки Т-29 прошли множество испытаний, в том числе и сравнительных с Т-28. По их итогам был сделан вывод, что Т-29, хотя и более сложен в производстве, но представляет большой интерес ввиду высокой скорости и хорошей маневренности.
По результатам испытаний в 1936 году на Кировском заводе изготовили эталонный образец Т-29. Планировалось в 1937 году развернуть его серийное производство, из-за чего даже была сокращена программа выпуска Т-28, однако ввиду большого количества недостатков Т-29 в своём имеющемся виде военных не удовлетворял. Согласно постановлению ГКО при СНК СССР № 14сс от 25 мая 1937 года, завод должен был переработать проект танка и разработать новый образец, с утолщёнными бронелистами из цементированной брони, установленными наклонно.
Эта машина, обозначенная как Т-29-Ц, была разработана под руководством Н. В. Цейца в рекордные сроки и уже 4 июля представлена на рассмотрение ГКО. Проект сильно отличался от эталонного Т-29. Была удлинена ходовая часть, получившая 5 пар опорных катков (из них три ведущих и две управляемых) вместо 4 у эталонного Т-29. Машина весом 30 т защищалась 30-мм бронёй и была вооружена 76-мм пушкой Л-10, пятью пулемётами ДТ и двумя пулемётами ДК. Вооружение размещалось в трёх башнях. Экипаж составлял шесть человек.
Т-29-Ц получил одобрение военных, и к 1 июля 1938 года планировалось изготовить опытный образец, но осенью 1937 года все работы в этом направлении были неожиданно свёрнуты, а Кировский завод продолжил выпускать танки Т-28 в прежнем объёме. Причины этого не совсем понятны, но, по ряду данных, такое решение было связано с арестом Н. В. Цейца как «вредителя» в сентябре 1937 года.